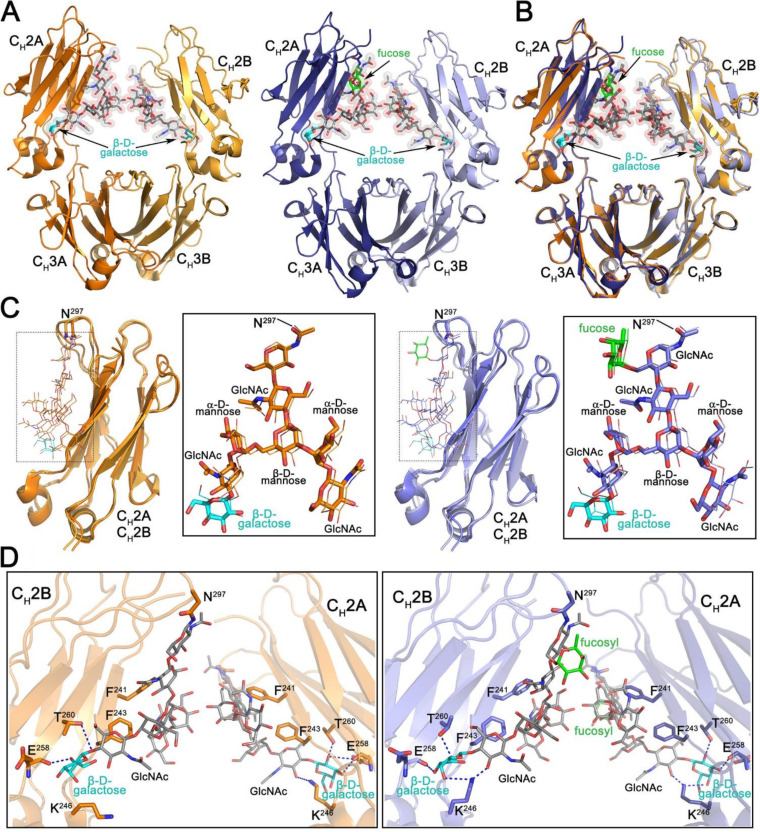
FIG 6.
Structural characterization of the Fc regions of N. benthamiana-produced PGT121. (A) Crystal structures of afucosylated (right) and fucosylated (left) Fc. The overall structure is shown in a ribbon diagram with the two heavy chains (CH2-CH3 domains) in lighter (chain B) and darker (chain A) shades of orange and blue for afucosylated and fucosylated variants, respectively. The sugars attached to asparagine 297 are shown as sticks and spheres colored by atom type (gray for carbon, red for oxygen, and blue for nitrogen). The fucose in the fucosylated Fc is colored green and the terminal galactose visible on the α6 arm of the glycan in both structures cyan. (B) Superposition of the afucosylated and fucosylated CH2-CH3 dimer (Fc domain) colored as in panel A. (C) Superposition of the CH2 domains from the afucosylated (left) and fucosylated (right) Fc dimer. Blow-up views to the right show the superposition of the glycan only with chain A shown as sticks and chain B as lines. Atom types are colored as in panel A. (D) Details of the glycan-glycan and glycan-protein contacts in the afucosylated (left) and fucosylated (right) Fc dimers. The glycan and interacting residues are shown as sticks and the protein backbone as a ribbon. Hydrogen bonds are shown with dashed lines. Atom types are colored as in panel A.