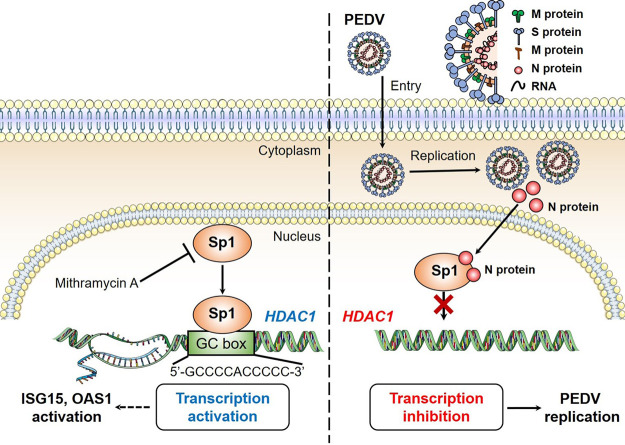
FIG 11.
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus inhibits expression of HDAC1 through interaction of its N protein with transcription factor Sp1. HDAC1 functions as an antiviral regulator by activating expression of antiviral genes, such as ISG15 and OAS1. The transcription factor Sp1 in the nucleus binds to the GC box in the HDAC1 promoter region. The Sp1-specific inhibitor, mithramycin A (MitA), suppresses transcription of HDAC1 by competitive binding to the GC box in the HDAC1 promoter. In the IPEC-J2 cells, PEDV replicates in the cytoplasm, where the viral N protein enters the nuclei via its nuclear localization sequence, 261-PKKNKSR-267. To escape the host innate immune response and promote self-replication, PEDV deploys its nuclear N protein to interact with the transcription factor Sp1 and prevent its further binding to the HDAC1 promoter, leading to decreased expression of HDAC1 and reduced expression of antiviral genes.