Figure 2.
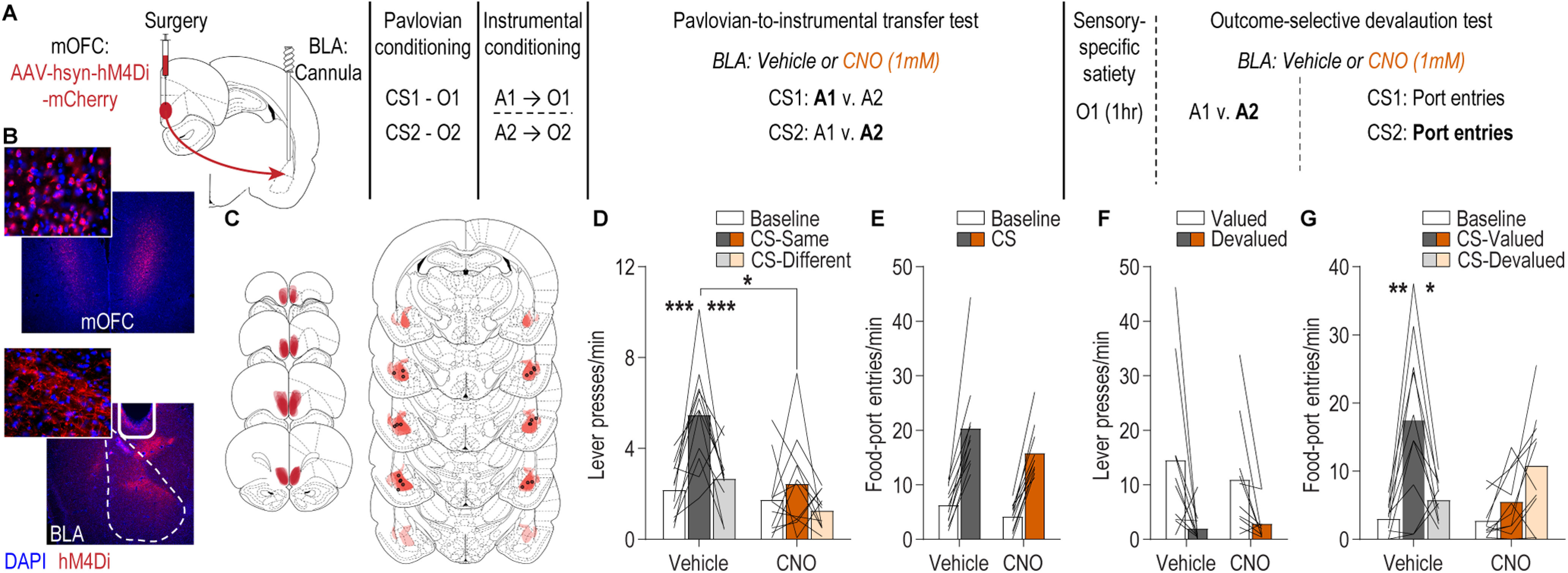
The mOFC→BLA pathway regulates the influence of stimulus-outcome memories over decision making and adaptive conditional responding. A, Schematic of behavioral training, testing, and chemogenetic inactivation strategy. CS, conditional stimulus (white noise or tone); O, outcome (sucrose solution or food pellet); A, action (left or right lever press). B, Representative fluorescent image of hM4Di-mCherry expression in mOFC cell bodies and immunofluorescent image of mOFC axons and terminals in the BLA near the implanted guide cannula. C, Schematic representation of hM4Di-mCherry expression in mOFC and axonal expression and injector tip placements in BLA for all subjects. D, Lever-press rate (lever presses/min) during the PIT test averaged across levers during the preCS baseline periods and during the CS periods on the lever earning the same outcome as the presented CS and the alternate lever (Different). Data are averaged across trials and CSs. E, Rate of entries into the food-delivery port (food-port entries/min) during the PIT test for the preCS baseline periods and during CS presentation (averaged across trials and CSs). F, Average lever-press rate during the instrumental choice phase of the outcome-specific devaluation test. Presses separated for those on the action that in training earned the valued versus devalued (prefed) reward. G, Rate of entries into the food-delivery port during the outcome-specific devaluation test, averaged across trials, during the preCS baseline period, and during presentation of the CS predicting the valued and devalued (prefed) rewards. Lines represent individual subjects. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
