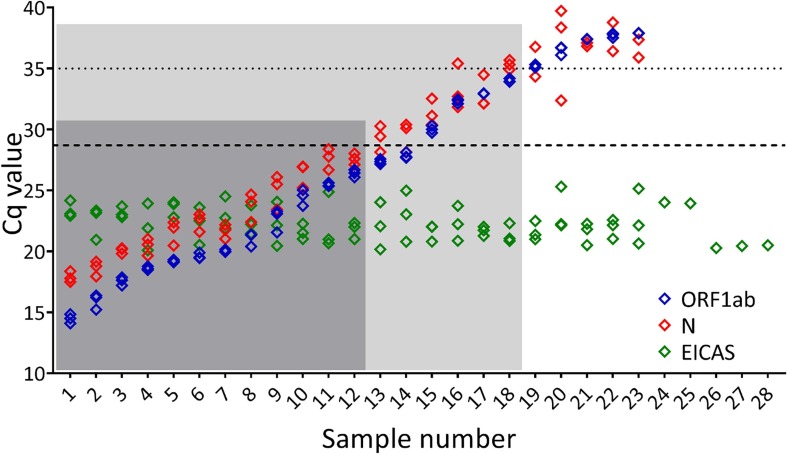
Fig. 1.
Effect of clinical sample on Cq. The CoV2-ID assay is a five-plex RT-qPCR that detects three SARS-CoV-2 targets: two non-structural replicase genes (Nsp10 and Nsp12) detected together (ORF1ab; blue diamonds) and the nucleocapsid gene (N; red diamonds), an extraction and inhibition control artificial sequence (EICAS; green diamonds) and a human target (JUN; data not shown). If ORF1ab with or without N amplifies with a Cq value it was reported as a positive (samples 1–23), while samples with absence of ORF1ab amplification were reported as negative (samples 24–28). The original data and full development of the CoV2-ID test are published in Bustin et al., 2020 [17]. The samples are ordered based on Cq value (low to high) with five negative samples giving a result for the EICAS only. Using a Cq of 35 as a hard cut off (horizontal dotted line), Samples 1–18 are reported as positive only (within light grey box). Placing the Cq threshold at its highest position on the amplification plots, which results in an increase in the Cq values of all samples moves the equivalent had cut off to a Cq of 28.7 and therefore reports only samples 1–12 as positive (within dark grey box). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)