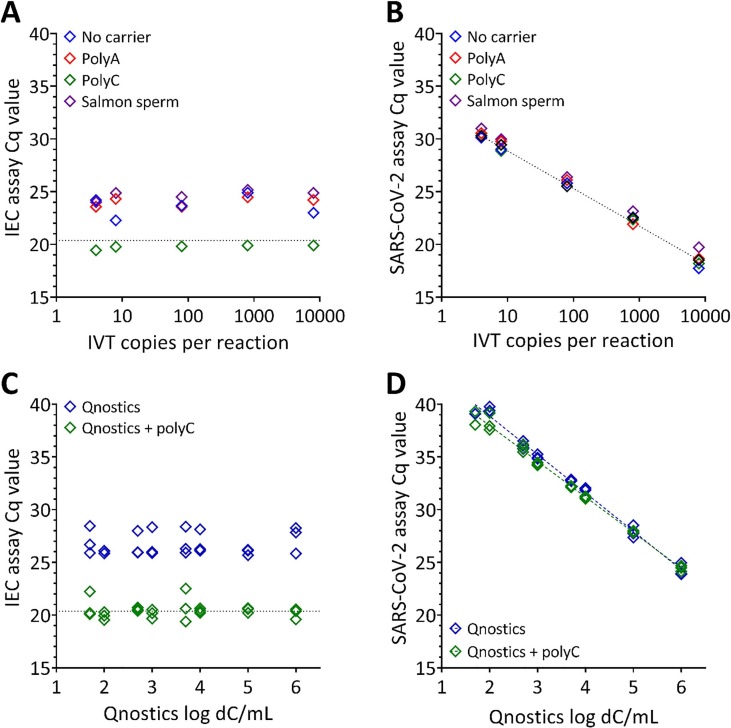
Fig. 3.
Effect of carrier molecules on Cq. (A-B) Duplex RT-qPCR of RNA extractions of a five-point dilution series of an IVT SARS-CoV-2 template RNA spiked with a constant amount of an internal RNA extraction control (IEC) in the presence of four different carrier conditions; PolyA, PolyC, Salmon Sperm gDNA (ssgDNA) or no carrier molecules. IVT copies per reaction are nominal and based on manufacturer’s reported concentration. (A) Cq values obtained by RT-qPCR of the IEC demonstrates that the inclusion of PolyC carrier molecules did not affect the Cq values obtained by direct addition to the RT-qPCR (dotted horizontal line). For all other carrier conditions, including no carrier, lower Cq values were observed. (B) Cq values obtained by RT-qPCR for the SARS-CoV-2 target were not affected by the addition of PolyA or PolyC carrier compared with the direct spike (diagonal dotted line). Higher Cq values were obtained with the ssgDNA carrier. (C-D) Duplex RT-qPCR of RNA extractions from a panel of commercially available, inactivated whole virus templates at eight different concentrations containing with either no carrier or PolyC carrier molecules. X-axes show the dC/mL based on the manufacturer’s reported concentration prior to extraction. (C) Cq values obtained for the IEC that was spiked into all samples at a constant concentration. There was a substantial difference in the Cq values between the two carrier conditions. (D) Cq values obtained for the SARS-CoV-2 target. There was no difference in the Cq of the matched viral inputs with or without PolyC.