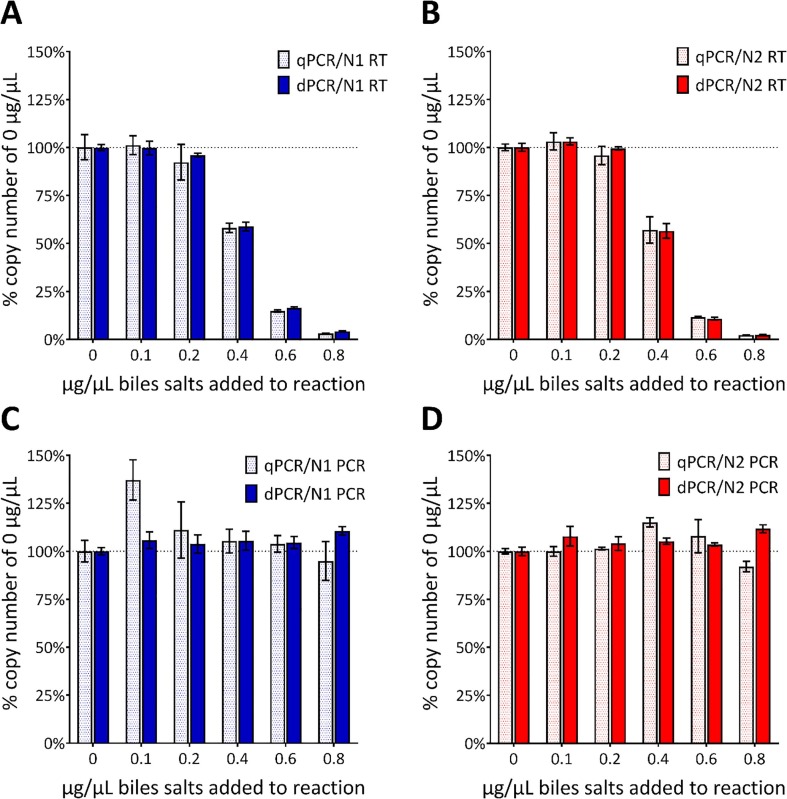
Fig. 4.
Effect of the addition of bile salts on copy number concentration. Bar graphs demonstrating the effect on the copy number concentration of adding increasing concentrations of bile salts to the RT-PCR reactions containing 1000 IVT EURM-019 copies/µL based on manufacturer’s reported concentration. Seven concentrations of bile salts (0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 µg/µL in the final reaction) were evaluated by qPCR (dotted bars) and dPCR (solid bars) and added either before the RT (A-B) or after the RT but before the PCR (C-D). Data is presented as the percentage of the copy numbers obtained from reactions containing no bile salts (horizontal dotted line and 0 µg/µL) with the error bars representing the standard deviation. (A-B) The measured concentration was reduced when ≥0.4 μg/µL bile salts is added as measured by both qPCR and dPCR with CDC N1 or N2 assays. There was no difference in copy number concentration regardless of assay or platform used. (C-D) There was no difference in copy number for any of the conditions based on data obtained by dPCR. For qPCR there was more variability in the copy numbers with an apparent enhancement when 0.1 µg/µl bile salts were added but inhibition when 0.8 µg/µL were added.