Figure 4.
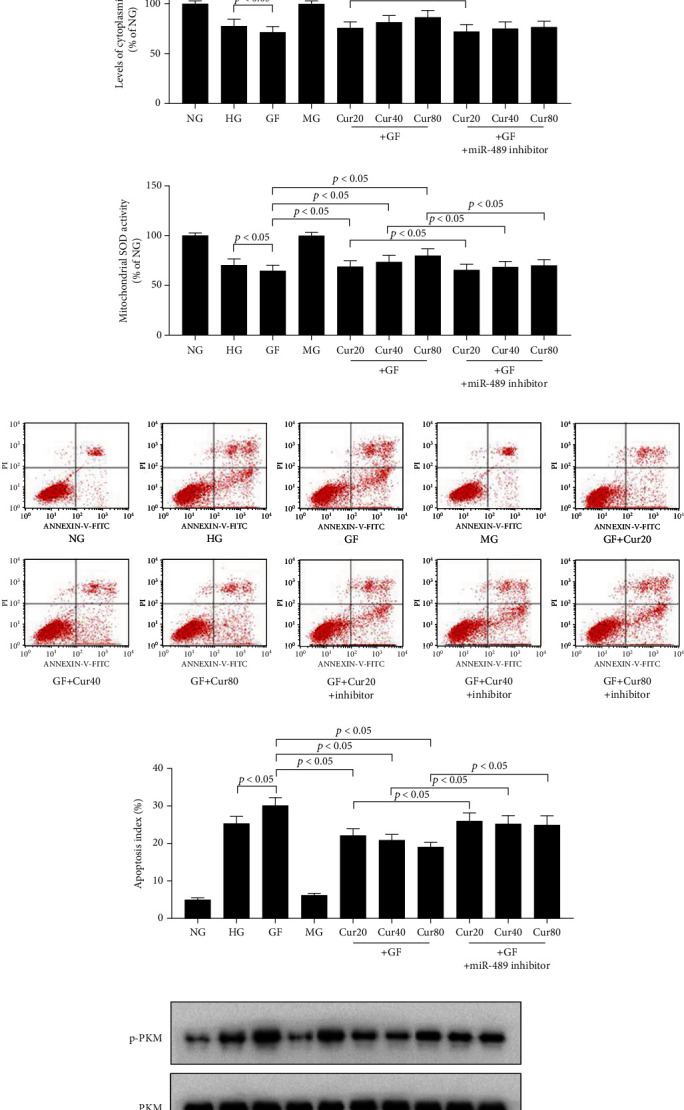
Cur prevented GF-triggered aerobic glycolysis by regulating miR-489 in HEK-293 cells. (a) RT-qPCR results showed that Cur could alleviate GF-induced reduction of miR-489 in a dose-dependent manner. (b) Inhibition effects of miR-489 inhibitor tested by RT-qPCR. (c) Viability of HEK-293 cells was tested by CCK8 at 48 h. (d) TNF-α and IL-1β at 48 h. (e) Levels of oxidative stress marker, including MDA and mitochondrial and cytoplasmic SOD at 48 h. (f) Apoptosis index was tested by flow cytometry at 48 h. Inhibitor of miR-489 could reduce Cur's protective effects in the fields of cell viability, inflammation injury, and oxidative stress. (g, h) The suppression of aerobic glycolysis by Cur treatment was prevented by the miR-489 inhibitor in HEK-293 cells. Each error bar reflects the SEM of at least three independent sets.
