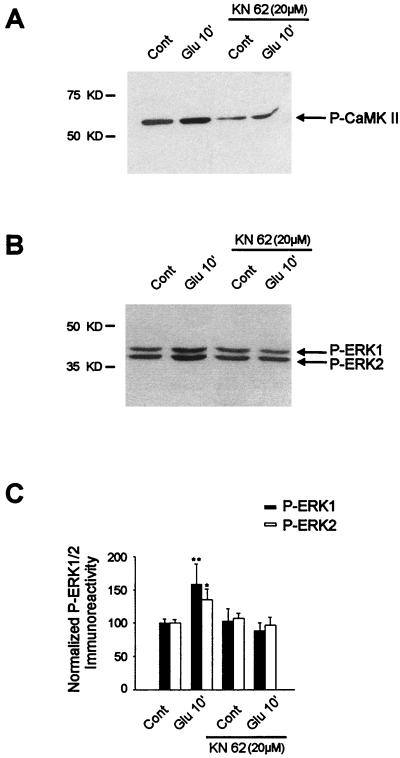
FIG. 7.
Role of the CaM-K inhibitor KN62 in glutamate-induced ERK activation. Striatal slices were superfused with KN62 (20 μM) for 30 min prior to and during glutamate application. (A) The efficacy of this compound was analyzed by Western blotting with an antiphospho-Thr286–CaM-KII antibody. Note that KN62 strongly decreases both basal levels and glutamate-induced phospho-Thr286-CaM-KII levels. (B) The same striatal extracts were analyzed with an anti-active ERK antibody. Note the inhibition of glutamate-induced ERK activation by KN62. (C) Densitometric measurements were performed in three independent experiments (representing nine striatal slices) in the presence or absence of KN62 (for each experiment, the inhibition of CaM-K activity by KN62 was verified as specified for panel A). Statistical analysis: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005 (unpaired Student’s t test) when comparing glutamate alone with control chambers.