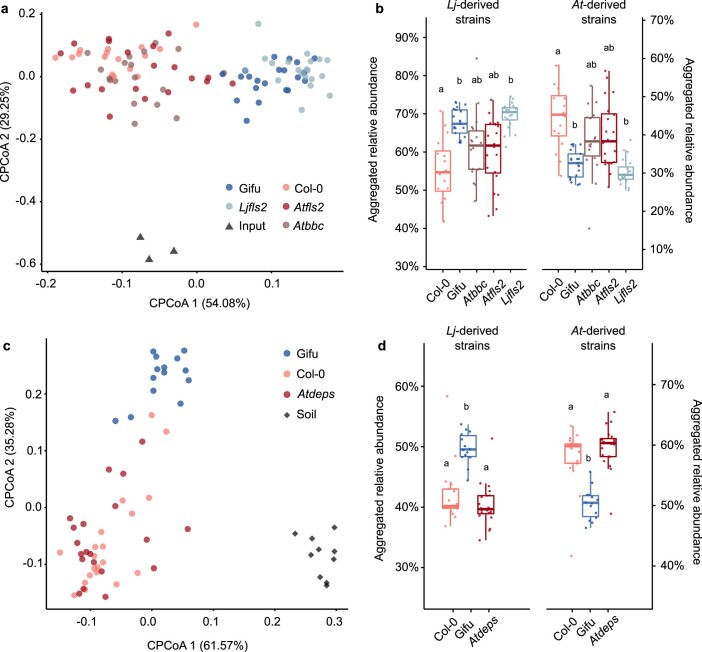
Extended Data Fig. 9. Tested plant immune receptors and signaling pathways do not affect host preference of commensals.
a, Constrained PCoA of Bray-Curtis dissimilarity (constrained by all biological factors and conditioned by all technical variables; n = 98; variance explained 24.6%, P = 0.001) of root samples from L. japonicus wild type Gifu, Ljfls2 mutant, A. thaliana wild type Col-0, Atfls2 mutant, and Atbbc mutant inoculated and grown with the mixed SynCom LjAt-SC1 (exp. G), and of the corresponding bacterial input communities. b, Aggregated relative abundance of the 16 Lj-derived and the 16 At-derived strains in the roots of Lotus and Arabidopsis plants. n = 21 for Gifu, n = 16 for Col-0, n = 20 for Ljfls2 and Atfls2, n = 18 for Atbbc. c, Constrained PCoA of Bray-Curtis dissimilarity (constrained by all biological factors and conditioned by all technical variables; n = 64; variance explained 42.2%, P = 0.001) of soil and root samples from Gifu, Col-0, and Atdeps mutant inoculated and grown with the mixed SynCom LjAt-SC3 (exp. H). d, Aggregated relative abundance of the 16 Lj-derived and the 16 At-derived strains in the roots of Lotus and Arabidopsis plants. n = 14 for Gifu, n = 20 for Col-0 and Atdeps. n refers to biologically independent samples.