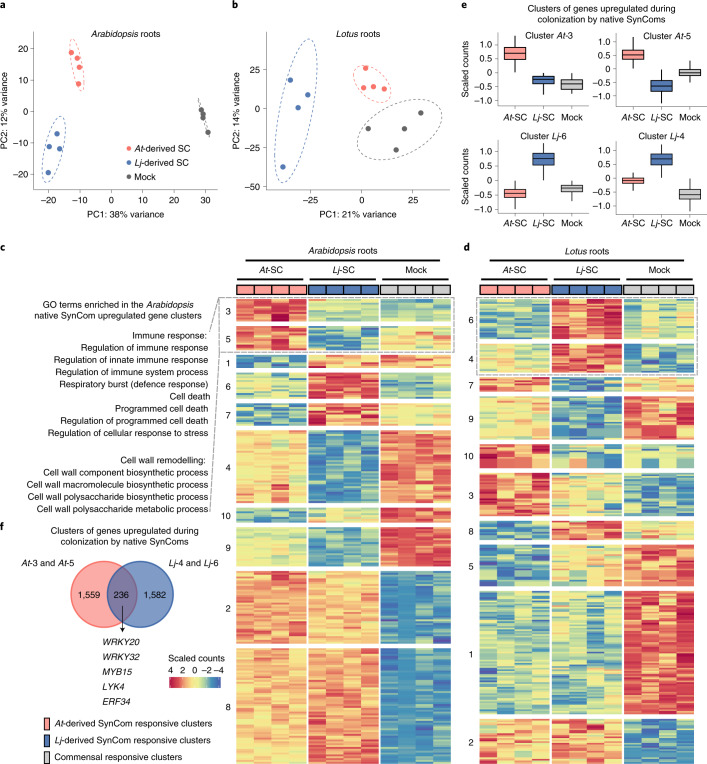
Fig. 4. SynCom-specific transcriptional outputs in Lotus and Arabidopsis roots.
a,b, Whole transcriptome-level principal component analysis of Arabidopsis (n = 12 biologically independent samples, a) and Lotus (n = 12, b) roots after coinoculation with host-specific SynComs (SC) (Lj- and At-SC3, exp. K). In the case of Lotus plants, a nodule isolate from the Lj-SPHERE collection was added to all treatments to prevent transcriptional outputs from being dominated by symbiosis or nitrogen starvation responses. c,d, Heatmaps showing scaled counts of genes arranged according to k-means clustering results (only differentially expressed genes shown) for Arabidopsis (c) and Lotus (d). e, Distribution of expression patterns for clusters of genes upregulated after coinoculation with native SynComs. f, Overlap in terms of homologues identified in the same clusters between the two host and a list of relevant transcription factors identified as potential key regulators of differential transcriptional responses.