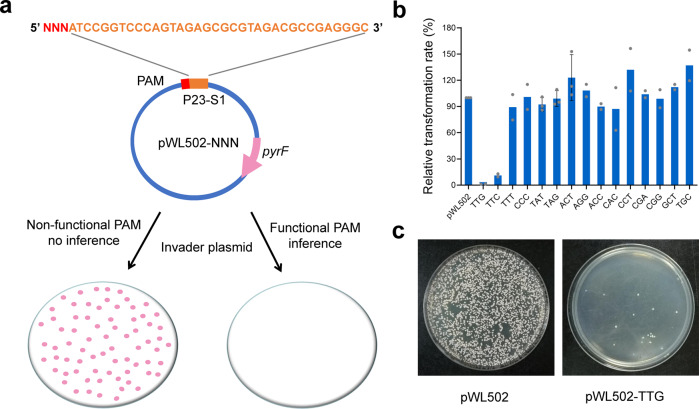
Fig. 2. Plasmid-based invader assay for identification of functional PAMs.
a The schematic representation of the plasmid-based invader assay. Potential PAM sequences (NNN) are introduced upstream of the spacer sequence P23-S1 (orange letters) and then inserted into pWL502 yielding invader plasmids pWL502-NNN. DF50ΔEPS is transformed with invader plasmids and selected on AS-168SY plates without uracil. Only the cells containing the invader plasmid with a non-functional PAM could grow on the plates. No cell growth indicates that the invader plasmid carries a functional PAM which leads to interference and degradation of the invader plasmid. b Relative transformation rates of PAM constructs. Transformation rates are calculated as the number of transformants/μg DNA. The transformation rate of pWL502 is used as the positive control. Data shown for two or three biological replicates. Error bars indicate SDs, n = 3. c Colonies obtained by transformation of 1 μg of plasmid pWL502 or pWL502-TTG.