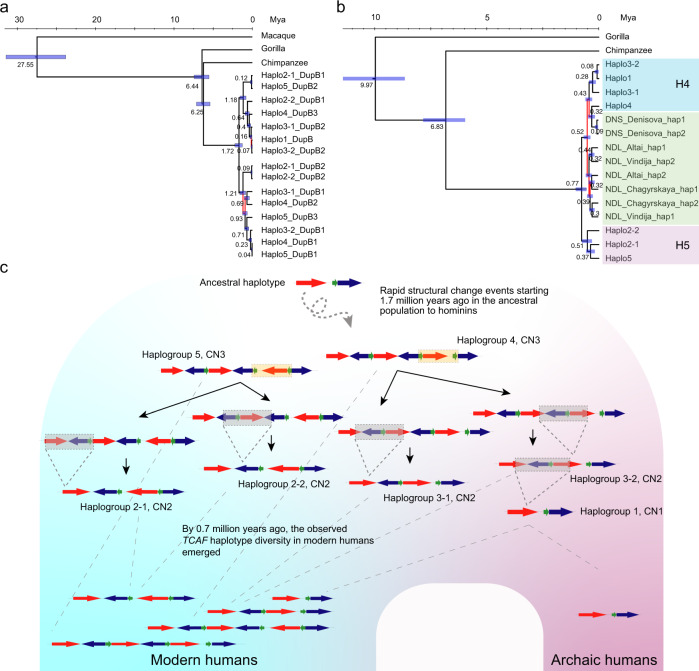
Fig. 4. Evolutionary reconstruction of TCAF structural diversity.
a Phylogeny of the haplogroups was inferred using TCAF DupB sequences and BEAST (v.2.6.2) with five independent runs of 10 million iterations of Markov Chain Monte Carlo (Methods). Numbers and horizontal bars at internal nodes indicate point estimates and 95% highest-posterior density intervals for the divergences (in million years ago, Mya), respectively. Branches with posterior probabilities <90% are colored in red. See Supplementary Figs. 22–24 for results of other SD sequences. b Inferred phylogeny of the modern human haplogroups and archaic hominin haplotypes using the 12 kbp unique sequences embedded within TCAF SDs (Fig. 1). Haplotypes of archaic samples were generated using high-confident single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) called within the unique diploid region. Phylogenetic inference was performed similarly as described above. c Schematic model for the evolution of TCAF haplotypes in humans based on phylogenetic inferences (Fig. 4a, b and Supplementary Figs. 22–24). Colored arrows are TCAF SDs; orange and gray areas indicate relative inversion and deletion events between haplogroups, respectively. Short dashed lines indicate putative breakpoints of structural changes between haplogroups, while the long-dashed lines illustrate lineage sorting.