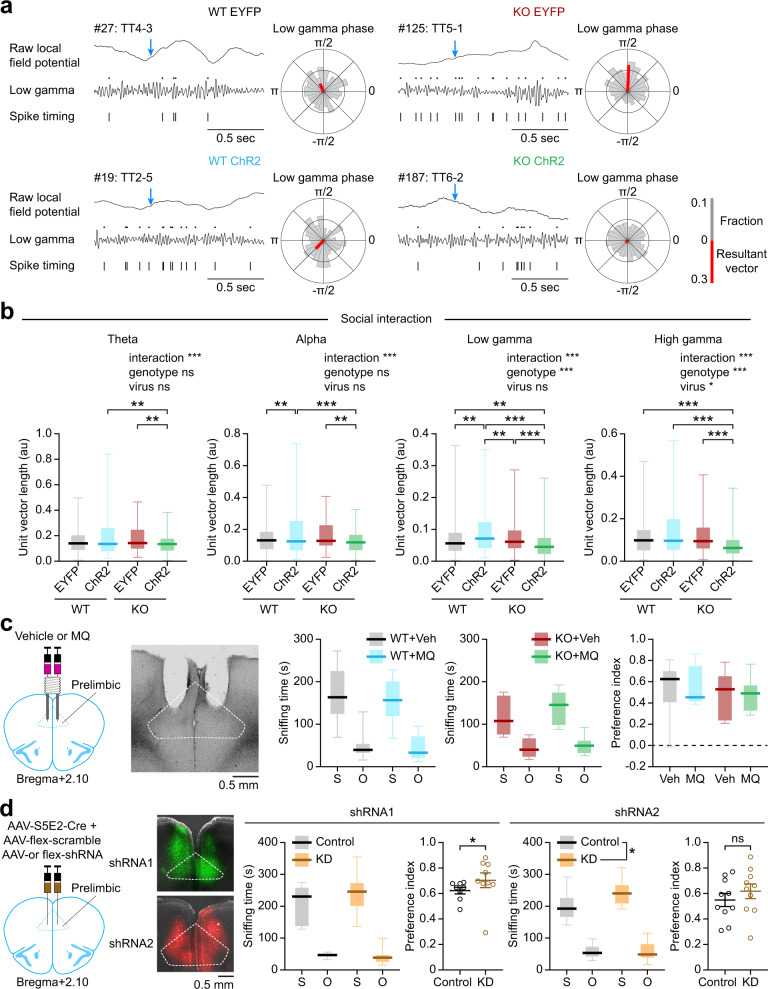
Fig. 9. Pv neuronal bursts suppress cortical spike-wave synchrony in the Shank2–/– mPFC, and Pv neuronal gap junctional inhibition moderately enhances social interaction in WT mice.
a Examples of spike-wave synchrony. Low-gamma oscillations extracted from raw LFPs were aligned with individual spikes to determine spike-wave synchrony. Arrows (blue), sniffing (nose-poke) onset for social target; rose plots, polar histograms of phase synchrony of a representative neuron during social interaction; red-colored bars, the sum of individual vectors. b Comparisons of spike-wave synchronies for the social target across different frequency ranges in the WT and Shank2–/– mPFC in the presence of Pv neuronal stimulation during social interactions. Data: minimal, maximal, median, 25%, and 75% values (n = 224 neurons from 7 mice for WT-EYFP, 91/8 [WT-ChR2], 145/4 [KO-EYFP], and 331/9 [KO-ChR2], **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test; interaction p = 0.0003, genotype p = 0.17, virus p = 0.7 [theta], interaction p < 0.0001, genotype p = 0.096, virus p = 0.939 [alpha], interaction p < 0.0001, genotype p = 0.096, virus p = 0.939 [low-gamma], interaction p < 0.0001, genotype p = 0.001, virus p = 0.025 [high-gamma]). c Direct mefloquine infusion (25 μM) into the mPFC of WT and Shank2–/– mice does not affect three-chamber social interaction, as shown by sniffing time for social/object targets and the social preference index ([social-sniffing time − object-sniffing time]/total sniffing time%). Data: minimal, maximal, median, 25%, and 75% values (n = 11 mice [T-Veh/vehicle] 11 [WT-MQ/mefloquine], 8 [KO-Veh], and 8 [KO-MQ], two-way RM-ANOVA). d Connexin-36 knockdown in Pv neurons in the mPFC of WT mice, using two independent shRNA constructs, moderately increases three-chamber social interaction. AAV-S5E2-Cre + AAV-flex-shRNA1/2-EGFP (or scrambled shRNA control) were injected into the WT mPFC at 14–16 [shRNA1] and 8–10 [shRNA2] weeks, followed by social-interaction tests after 2 weeks. Data: minimal, maximal, median, 25%, and 75% values (n = 8 [WT-control_1], 8 [WT-shRNA1], 9 [KO-control_1], and 9 [KO-shRNA1], 10 [WT-control_2], 10 [WT-shRNA2], 10 [KO-control_2], and 10 [KO-shRNA2], *p < 0.05, ns, not significant, two-way RM-ANOVA, two-tailed Mann–Whitney test, and two-tailed Student’s t-test; interaction p = 0.2335, treatment p = 0.3617, target p < 0.0001 [sniffing-shRNA1], p = 0.0274 [preference-shRNA1], interaction p = 0.1258, treatment p = 0.0303, target p < 0.0001 [sniffing-shRNA2], p = 0.3869 [preference-shRNA2]). See Source data for raw data values and Supplementary Table 1 for statistical details.