Figure 4:
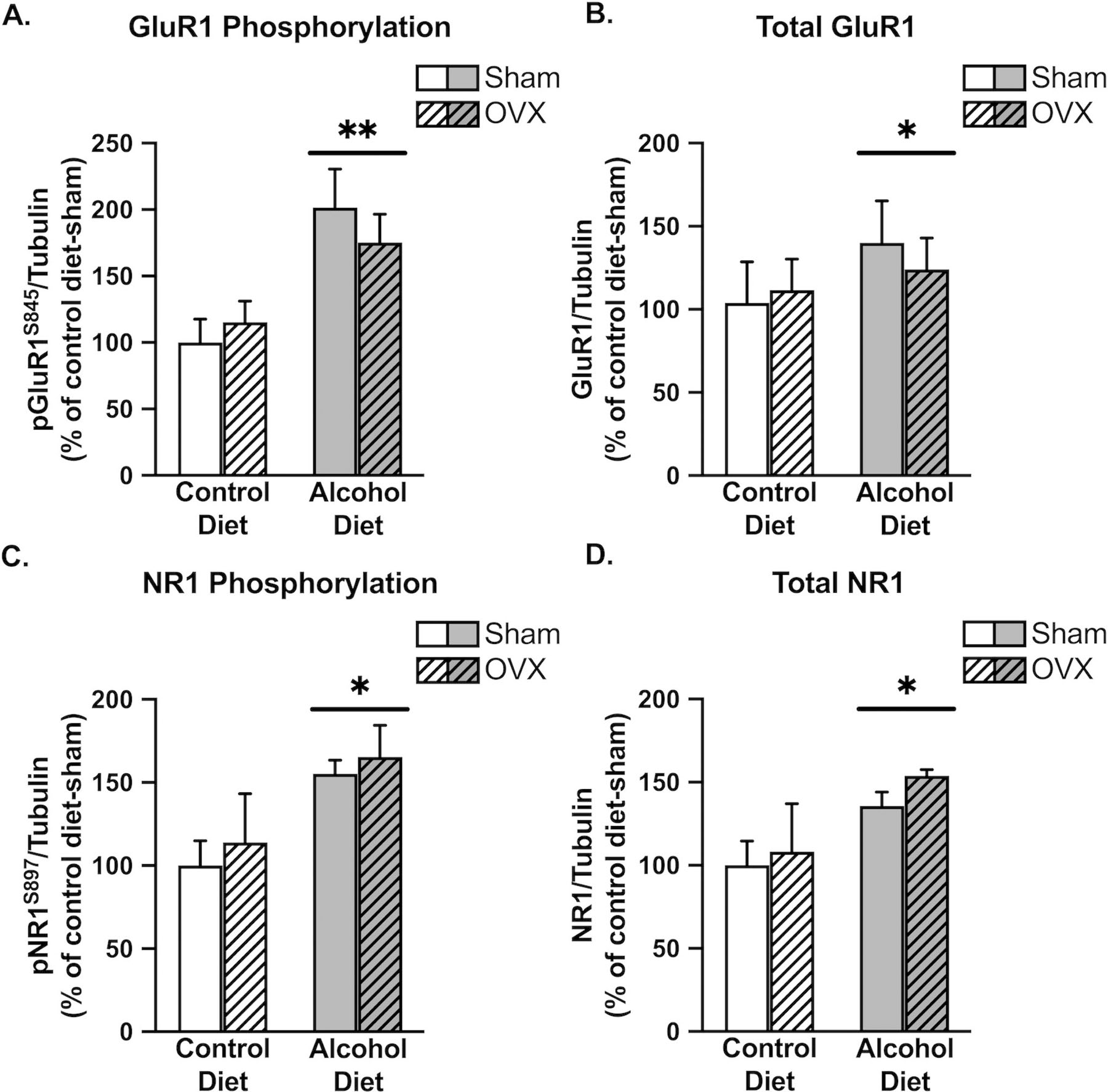
Chronic alcohol increases both phosphorylated and total levels of glutamate receptor channel subunits in the cingulate cortex. There was a significant main effect of alcohol to increase GluR1 phosphorylation (A; p=0.0018), total levels of GluR1 (B; p=0.0395), NR1 phosphorylation (C; p=0.0146), and total levels of NR1 (D; p=0.0354). Control diet + sham surgery, solid navy (n = 5); control diet + OVX, navy dotted (n = 5); alcohol diet + sham surgery, solid orange (n = 5); alcohol diet + OVX, orange dotted (n = 4).
