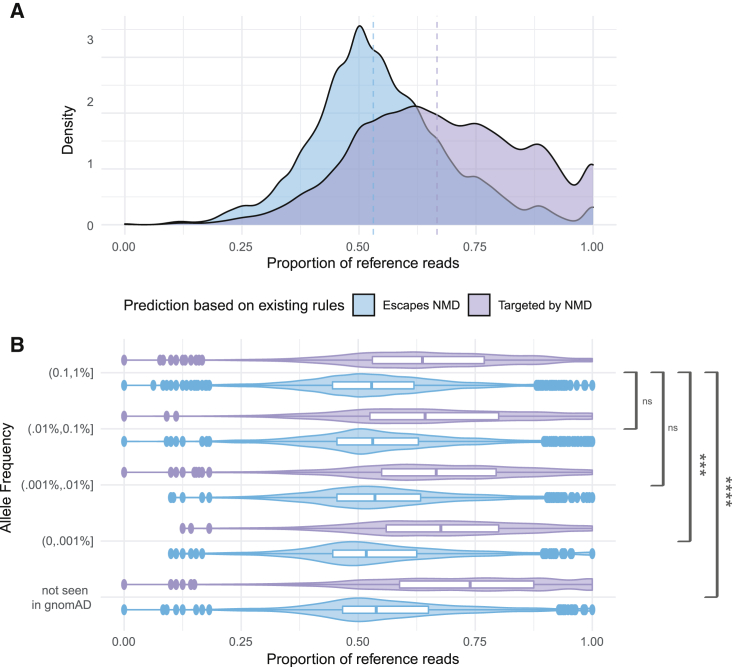
Figure 1.
Centrally located and rare truncating variants show stronger allelic imbalance
(A) Distribution of the proportion of reference reads for rare (genome aggregation database [gnomAD] minor allele frequency [MAF] ≤ 1%) protein truncating variants for those predicted by the positional rules defined in Lindeboom et al.8 to escape NMD (light blue) or trigger NMD (light purple). Medians indicated by dashed lines.
(B) Distribution of rare stop variants for variants predicted to escape NMD (light blue) or trigger NMD (light purple) by gnomAD allele frequency. Boxplots show mean and interquartile range. Brackets show the significance of the difference in differences test between each prediction type across decreasing allele frequencies; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.00001; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.