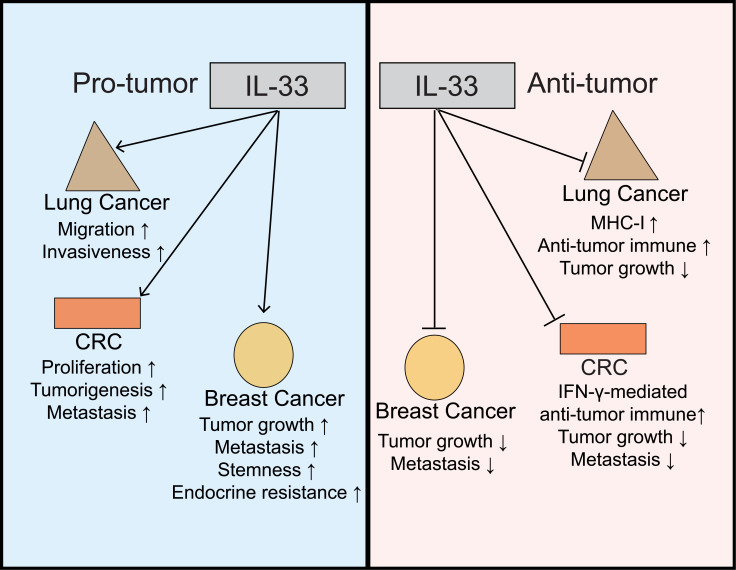
Fig. (3).
Opposite functions of IL-33 in tumors. For example, in lung cancer, CRC, and breast cancer, as shown on left, IL-33 can promote tumorigenesis, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance. On the right, IL-33 inhibits tumors by enhancing the anti-tumor immune response mediated by MHC-1 or IFN-γ. CRC: colorectal cancer. Drugs including FR901464 (SSA), meayamycin B targeting SF3B1, isoginkgetin and 1, 4-heterocyclic, which are involved in step 1 and step 2 splicing [10]. Thus, manipulating AS is a promising immunotherapeutic target with potential research value. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).