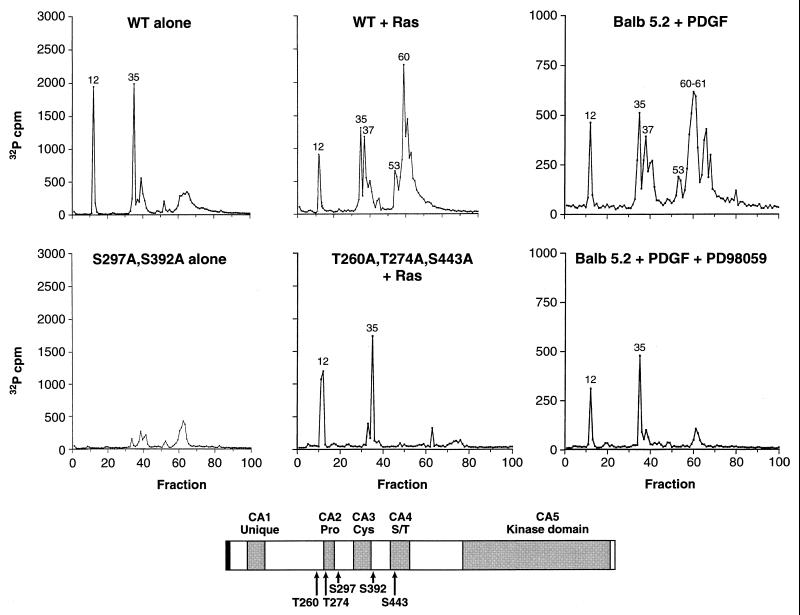
FIG. 1.
Identification of in vivo sites of KSR phosphorylation. In vivo 32P-labeled KSR proteins were isolated from 293 cells expressing WT KSR alone (WT alone), coexpressing WT-KSR and activated Ras (WT + Ras), expressing S297A,S392A-KSR alone (S297A,S392A alone), or coexpressing T260,T274A,S443A-KSR and activated Ras (T260,T274A,S443A + Ras) and from BALB 5.2 cells treated for 5 min with PDGF (Balb 5.2 + PDGF) or treated with PDGF in the presence of the MEK inhibitor PD98059 (Balb 5.2 + PDGF + PD98059). Isolated KSR proteins were digested with trypsin, and the resulting tryptic phosphopeptides were separated and eluted from a reversed-phase HPLC C18 column. The amount of 32P radioactivity collected in each fraction is shown. Tryptic phosphopeptides contained within fractions 12 and 35 of WT KSR corresponded to S297 and S392, respectively. In the presence of Ras, tryptic phosphopeptides contained within fractions 37, 53, and 61 of WT KSR corresponded to T260, T274, and S443, respectively. The schematic representation of KSR shows the locations of S297, S392, T260, T274, and S443. The gray boxes represent the five conserved areas (CA1 to CA5) of the KSR family members. Pro, Cys, and S/T indicate that the corresponding CA regions are rich in proline, cysteine, and serine/threonine residues, respectively.