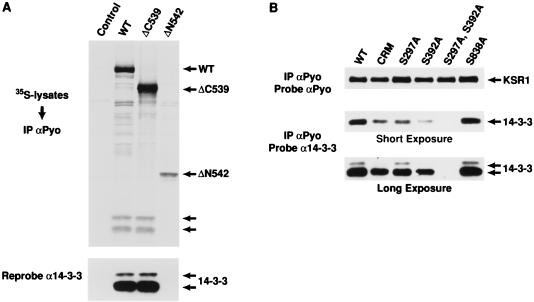
FIG. 2.
The constitutive in vivo sites of KSR phosphorylation are binding sites for 14-3-3. (A) 293 cells expressing full-length WT KSR, the isolated amino-terminal domain of KSR (ΔC539), or the isolated catalytic domain (ΔN542) were labeled with [35S]methionine and lysed in NP-40 buffer. The KSR proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with αPyo, resolved by SDS-PAGE (10% gel), and transferred to nitrocellulose. The resulting proteins were examined by autoradiography (top). The positions of WT, ΔC539, and ΔN542 KSR proteins are indicated by arrows, as are proteins with a predicted molecular mass of 30 and 32 kDa. The nitrocellulose membrane was then examined by immunoblot analysis using a 14-3-3 antibody (α14-3-3) to identify the 30 and 32-kDa proteins as 14-3-3 isoforms (bottom). (B) 293 cells expressing WT KSR, CRM (C359S,C362S)-KSR, and S297A-, S392A-, S297A,S392A-, and S838A-KSR proteins were lysed in NP-40 buffer and immunoprecipitated with αPyo. The resulting immunoprecipitates were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE (10% gel) and examined by immunoblot analysis using α14-3-3. Short and long exposures are shown. The membrane was then reprobed with αPyo to demonstrate that the expression levels of the KSR mutant proteins were equivalent.