Figure 3.
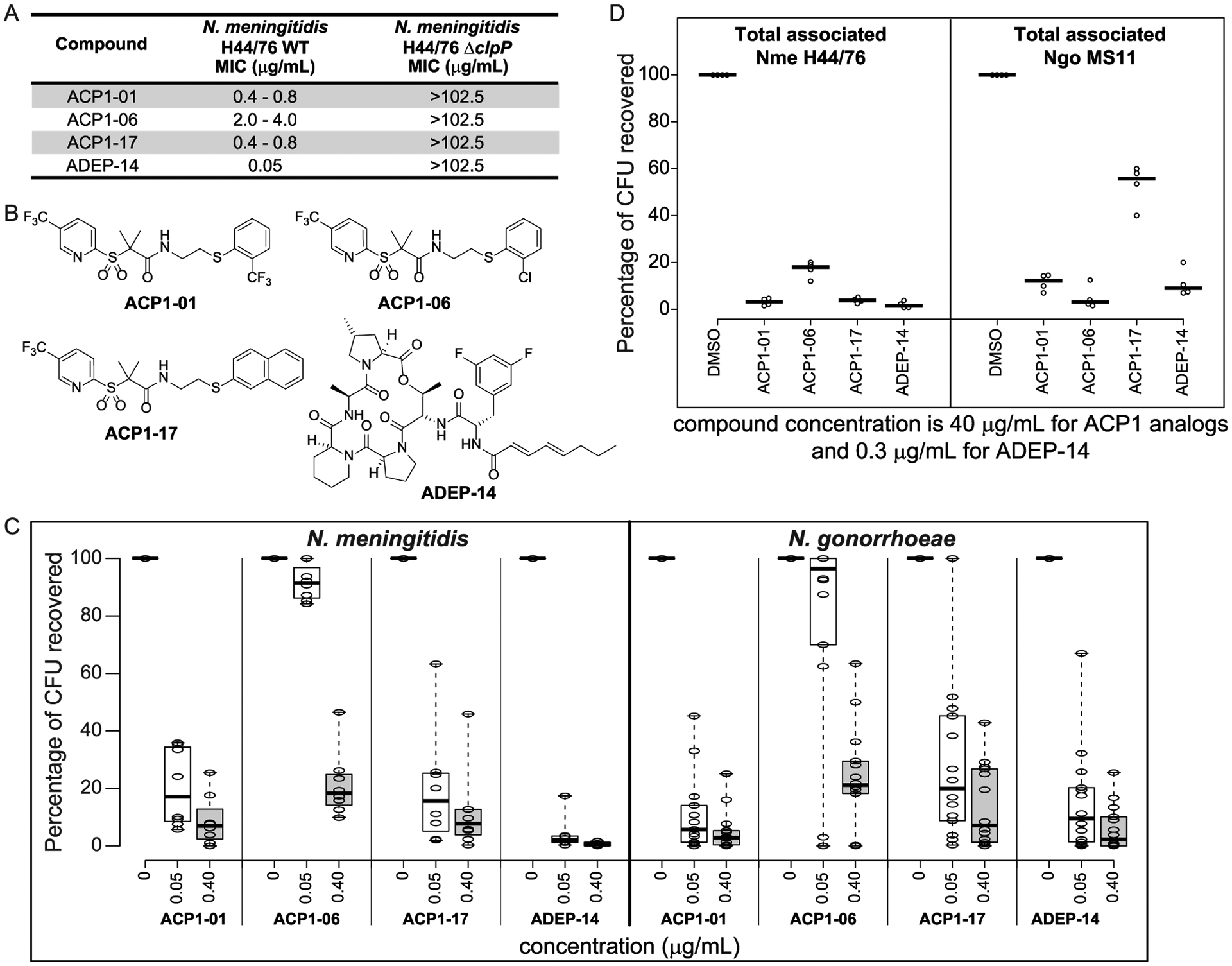
Antibacterial activity of ACP1-01, ACP1-06, ACP1-17, and ADEP-14. (A) Minimum inhibitory concentrations of selected analogues on the growth of WT N. meningitidis H44/76 compared to N. meningitidis H44/76 ΔclpP. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown. (B) Chemical structures of ACP1-01, ACP1-06, ACP1-17, and ADEP-14. (C) Shown are boxplots indicating the antibacterial susceptibility of various meningococcal (8 strains) and gonococcal (14 strains) reference strains to ACP1-01, ACP1-06, ACP1-17, and ADEP-14 after 20 h of treatment. Percent CFUs recovered was calculated as (CFUs recovered after treatment)/(CFUs of untreated bacteria) × 100. A total of three experiments were performed for each strain tested at each concentration of test compounds. The individual values were then averaged and converted to percentage CFU recovered. Treatment concentration resulting in less than 20% CFUs was considered as concentration at which strains were susceptible to the test compound. Boxplots were generated using BoxPlotR (http://shiny.chemgrid.org/boxplotr/). Thick horizontal lines represent the median. Whiskers extend to minimum and maximum values. (D) Effect of compounds on in vitro Neisserial infection. HeLa cells expressing human CEACAM1 or CEACAM5 were infected for 4 h with N. meningitidis H44/76 or N. gonorrhoeae MS11, respectively, and then treated with the indicated compounds at a final concentration of 40 μg/mL for ACP1 analogues and 0.3 μg/mL for ADEP-14 for 2 h, or with 1% DMSO for 2 h as a solvent control. CFUs recovered after treatment are reported as percent of CFUs observed after plating HeLa cell lysates obtained after treatment with saponin and pipetting to break the human cell membranes. Experiments were repeated four times and the thick horizontal lines represent the median.
