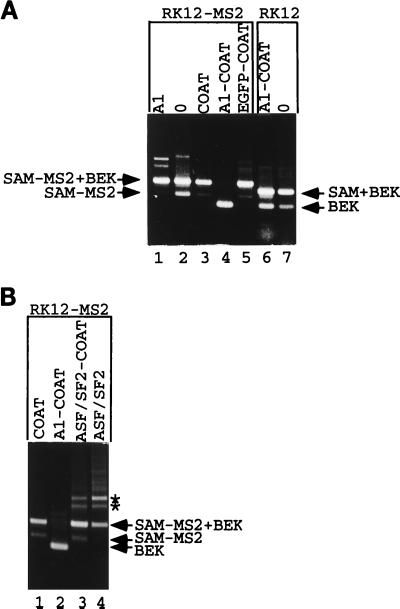
FIG. 5.
Recruitment of hnRNP A1 represses splicing. (A) RK12-MS2 was cotransfected into 293 cells with an expression vector coding for hnRNP A1 (lane 1), with the empty expression vector ΔCOAT (lane 2), or with expression vectors coding for coat (lane 3), an hnRNP A1-coat fusion (lane 4), or an EGFP-coat fusion (lane 5). RK12 was cotransfected into 293 cells with an expression vector coding for an hnRNP A1-coat fusion (lane 6) or the empty expression vector ΔCOAT (lane 7). Harvested RNA was subjected to RT-PCR with P1 and P2, and products were separated by gel electrophoresis. The origins of various fragments obtained are shown. The structures of named fragments are shown in Fig. 1A (for SAM+BEK [0.5 kb] and BEK [0.35 kb]) or Fig. 4 (for SAM-MS2 [0.45 kb] and SAM-MS2+BEK [0.6 kb]). (B) RK12-MS2 was cotransfected into 293 cells with the coat expression vector (lane 1) or with expression vectors coding for the hnRNP A1-coat fusion (lane 2), an ASF/SF2-coat fusion (lane 3), or ASF/SF2 devoid of any coat sequences (lane 4). Harvested RNA was analyzed as described for panel A. Asterisks mark two RT-PCR products discussed in the text which appear after overexpression of ASF/SF2 activity.