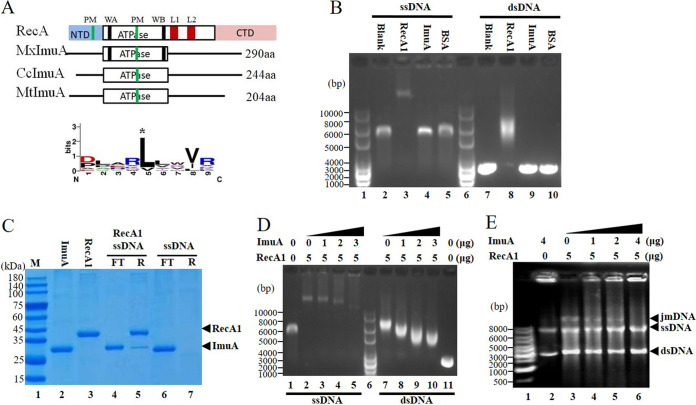
FIG 4.
ImuA function analysis. (A) Comparison sketch of ImuA proteins. RecA, E. coli RecA; MxImuA, M. xanthus ImuA; CcImuA, C. crescentus ImuA; MtImuA, M. tuberculosis ImuA; PM, polymerization motif; WA, Walker A motif; WB, Walker B motif; L1 and L2, DNA-binding loops 1 and 2; NTD, N-terminal domain; aa, amino acids. (B) DNA-binding ability. RecA1 was used as a positive control, and bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used as a negative control. (C) Ability of ImuA to bind to RecA1-coated single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA fixed on Sepharose resin was prebound with excess RecA1 protein. ImuA was added to the RecA1-coated ssDNA. SDS-PAGE was used to detect the unbound ImuA protein in the flowthrough (FT) and ImuA/RecA proteins bound to resin (R). (D) Effects of increased concentrations of ImuA on the binding of RecA1 to DNA. (E) Effects of ImuA on the recombinase activity of RecA1. jmDNA, joint molecular DNA; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA.