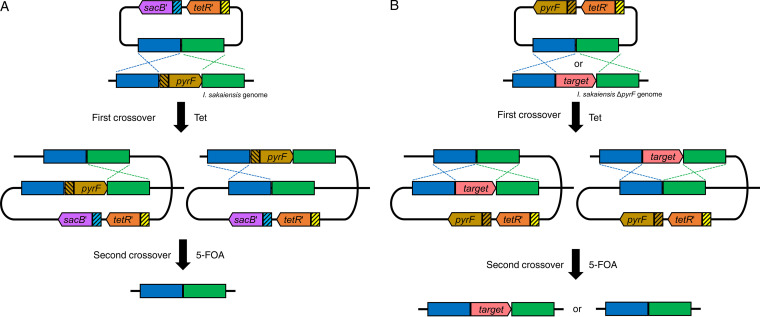
FIG 1.
Schematic diagrams of targeted gene disruption by homologous recombination in I. sakaiensis. (A) Disruption of pyrF and its promoter. The first crossover occurs at either the 5′-flanking region or 3′-flanking region of the target. In the resultant mutants, the second crossover produces the ΔpyrF strain (parent strain). (B) Disruption of petase and mhetase. The first crossover occurs at either 5′-flanking region or 3′-flanking region of the disruption target. The second crossover potentially produces the parent strain or the target gene disruption strain. Yellow and light blue boxes with slant lines indicate the original promoters of tetR and sacB, respectively, in pT18mobsacB. Brown box with slant lines indicates original promoter of pyrF in I. sakaiensis genome. Blue and green boxes indicate 5′- and 3′-flanking regions of the disruption target, respectively. 5-FOA, 5-fluoroorotic acid; pyrF, orotidine 5′-phosphate decarboxylase gene; sacB′, levansucrase gene with codon optimization for expression in the genus Ideonella; Tet, tetracycline; tetR′, tetracycline repressor protein gene with codon optimization for expression in the genus Ideonella.