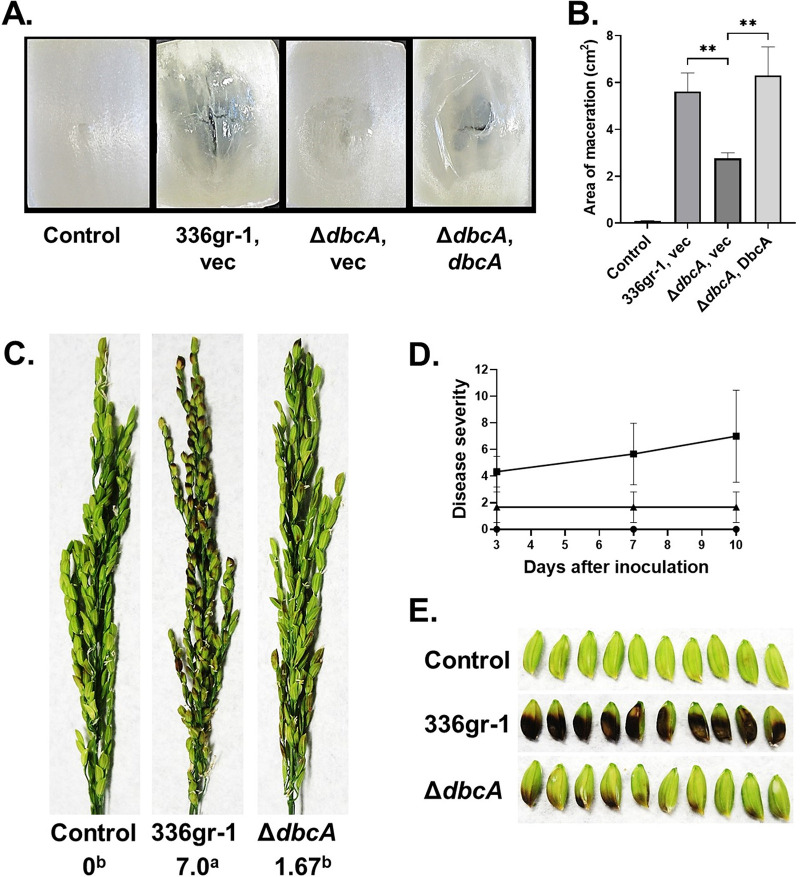
FIG 2.
B. glumae ΔdbcA strain is compromised for virulence in onion slices and rice panicles. (A) The area of maceration on onion slices indicates the virulence phenotype for each bacterial strain. Onion slices were infected with equal amounts of cells from B. glumae 336gr-1 transformed with control vector (vec) and the B. glumae ΔdbcA strain transformed with control vector (vec) and pSC501 (dbcA). Onion slices were incubated at 30°C for 72 h in a humid chamber. (B) Area of maceration (cm2) produced by indicated strains. **, P < 0.01. (C) Rice seed discoloration (black necrosis) indicates the virulence phenotype for control (water), B. glumae 336gr-1, and the ΔdbcA strain. The images were taken 10 days postinoculation, and disease severity score was determined with a 0 to 9 scale. Different letters below the score indicate statistical significance. (D) The line graph shows the disease progress for rice panicles inoculated with water (circles), B. glumae 336gr-1 (squares), and the ΔdbcA strain (triangles) at 3, 7, and 10 days postinoculation. (E) Detailed view of seed discoloration produced by control, B. glumae 336gr-1, and the ΔdbcA strain at 10 days postinoculation.