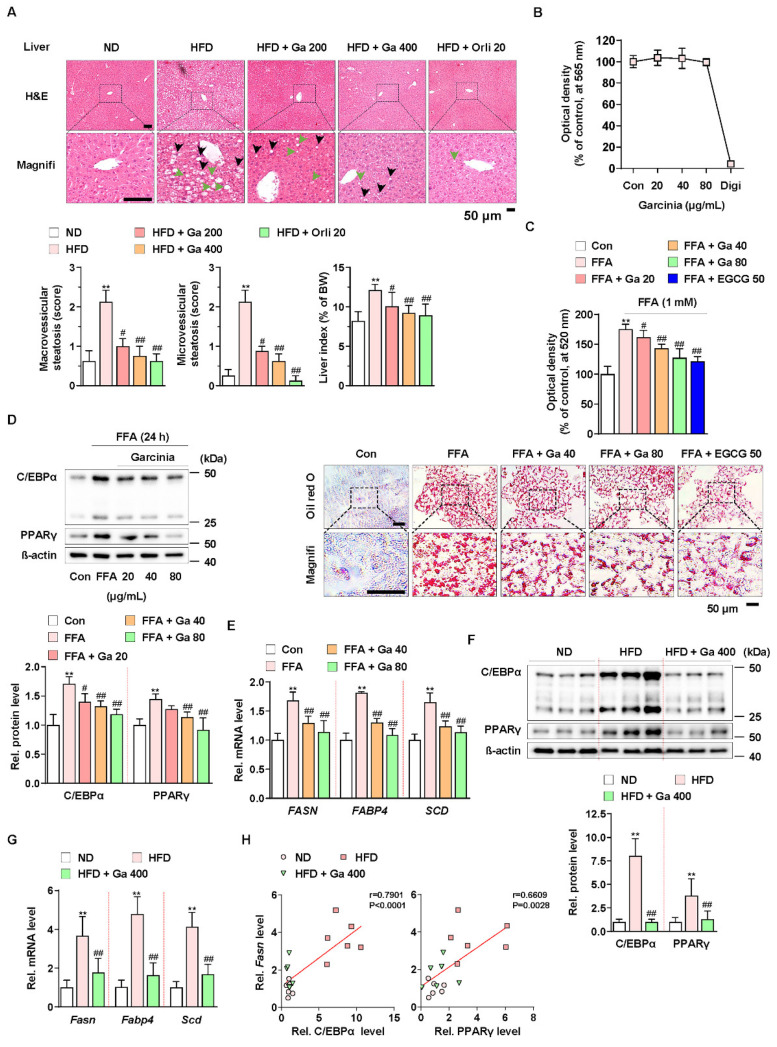
Figure 1.
Anti-NALFD effect of Garcinia cambogia in HFD-fed mice reducing hepatic steatosis. (A) Representative images showing the effect of G. cambogia (Ga, 200 and 400 mg/kg) on HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. H&E staining of liver tissues was performed. The scores of macrovesicular (black arrow) and microvesicular (green arrow) steatosis and liver index were quantified, as described in the Methods section. Normal diet (ND)-fed mice were used as the negative control for high levels of fat accumulation, and orlistat (20 mg/kg) was used as the positive control for anti-obesity and anti-steatosis effects (n = 7 per group). Scale bars: 50 μm. Magnifi: magnification. ** p < 0.01 vs. ND-fed mice, # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 vs. HFD-fed mice. (B) MTT assay showing the effect of G. cambogia (20–80 μg/mL) on cell viability. HepG2 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of G. cambogia and digitonin (100 μg/mL, positive control) for 24 h (n = 5 per group). (C) oil red O assay and representative images showing the effect of G. cambogia (20–80 μg/mL) on free fatty acid (1 mM FFA)-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. FFA-induced HepG2 cells were treated with G. cambogia and EGCG (50 μM, positive control) for 24 h (n = 5 per group). Scale bar: 50 μm. Magnifi: magnification. ** p < 0.01 vs. Con, # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 vs. FFA. Effect of G. cambogia (20–80 μg/mL) on (D) C/EBPα and PPARγ expression and (E) transcript levels of FASN, FABP4, and SCD in FFA-treated HepG2 cells (d, n = 4 per group; e, n = 5 per group). Effect of G. cambogia on (F) C/EBPα and PPARγ expression and (G) Fasn, Fabp4, and Scd transcript levels of liver tissues from ND-fed, HFD-fed, and HFD-fed mice administered a high dose of G. cambogia (400 mg/kg) (n = 6 per group). (H) Correlations between Fasn transcript and C/EBPα and PPARγ protein levels in liver tissues (n = 6 per group). Each point represents one sample. Data are mean ± S.D.