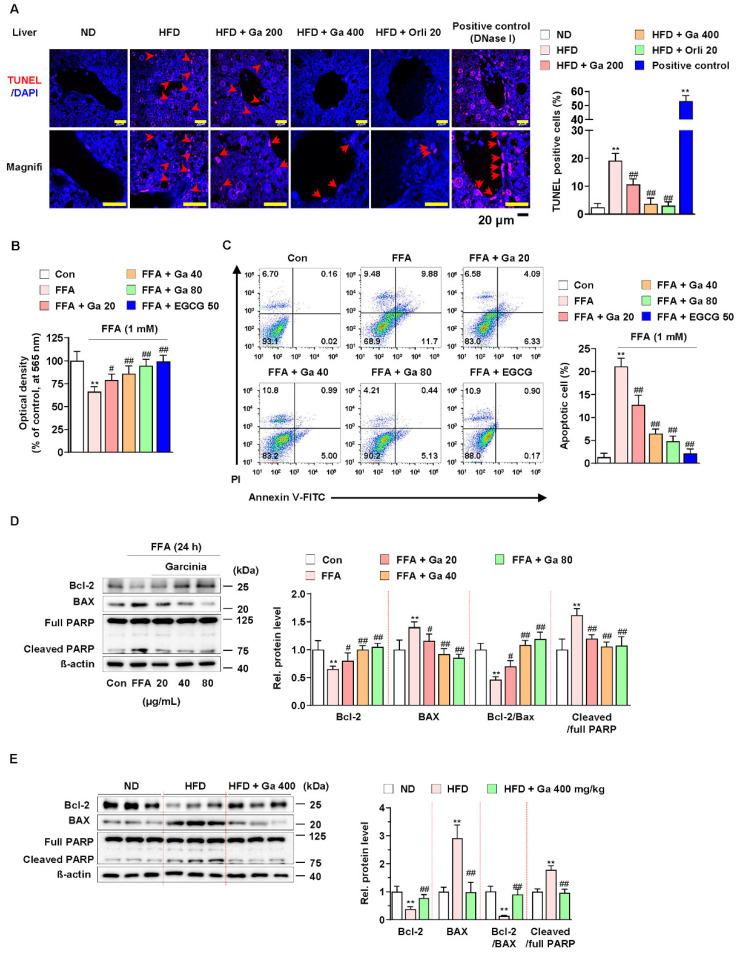
Figure 2.
Effect of Garcinia cambogia on HFD-induced apoptosis in the liver. (A) Representative images of TUNEL staining and quantification data for the number of TUNEL-positive cells in HFD-induced liver tissues. Positive control: DNase I (30 U) treated group. Scale bar: 20 μm. (n = 6 per group). Magnifi: magnification. ** p < 0.01 vs. ND-fed mice, ## p < 0.01 vs. HFD-fed mice. (B) MTT assay showing the effect of G. cambogia on FFA-induced cell viability. Cells were treated with G. cambogia (20–80 μg/mL) and EGCG (50 μM) for 24 h (n = 5 per group). ** p < 0.01 vs. Con, # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 vs. FFA. (C) Effect of G. cambogia on apoptosis in FFA-treated HepG2 cells. Cells were treated with G. cambogia (20–80 μg/mL) and EGCG (50 μM) for 24 h (n = 4 per group). The numbers of negatively and positively stained cells are expressed as percentages of the total number of cells. (D) Effect of G. cambogia on Bcl-2 and BAX expression and PARP cleavage in FFA-treated HepG2 cells (n = 4 per group). (E) Effect of G. cambogia on Bcl-2 and BAX expression and PARP cleavage of liver tissues from ND-fed, HFD-fed, and HFD-fed mice administered a high dose of G. cambogia (400 mg/kg) (n = 6 per group). Data are mean ± S.D.