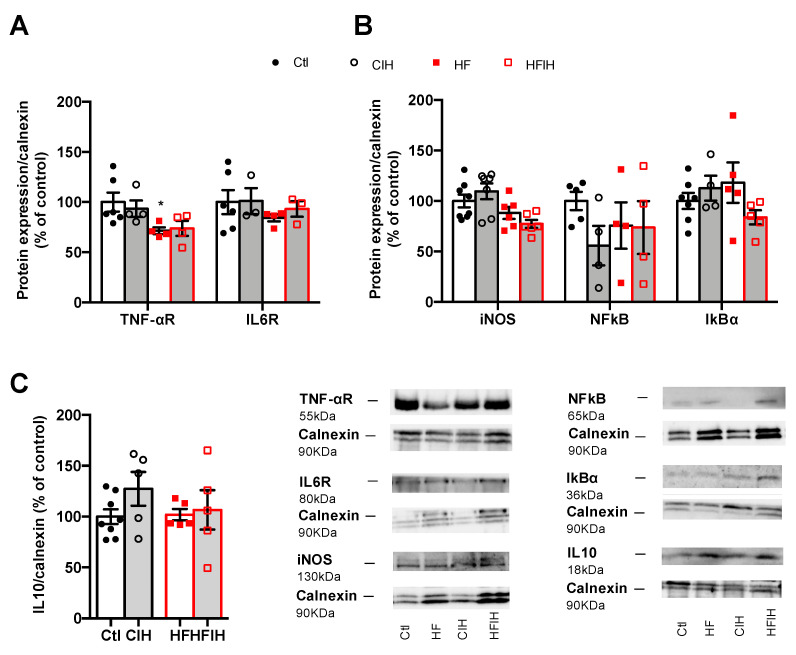
Figure 5.
Effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH/IH) on adipose tissue inflammation in control and high-fat (HF) animals. (A) Effect of severe CIH on interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R, 80 kDa) and tumor necrosis factor alfa receptor (TNF-αR, 55 kDa) immunoreactivity in control and HF animals in relation to the expression of the loading protein, calnexin (90 kDa). (B) Effect of severe CIH exposure on inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, 130 kDa), nuclear factor k B (NFkB, 65 kDa), and light polypeptide of nuclear factor k B ɑ (IkBɑ, 36 kDa) immunoreactivity in control and HF animals in relation to the expression of the loading protein, calnexin (90 kDa). (C) Effect of severe CIH on interleukin 10 (IL10, 18 kDa) immunoreactivity in control and HF animals in relation to the expression of the loading protein, calnexin (90 kDa). Representative Western blots for each protein studied are depicted in the right panel below. Data are presented as means ± SEM of 4–8 animals. One- and two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s and Bonferroni multiple comparison tests, respectively: * p <0.05, compared with control animals.