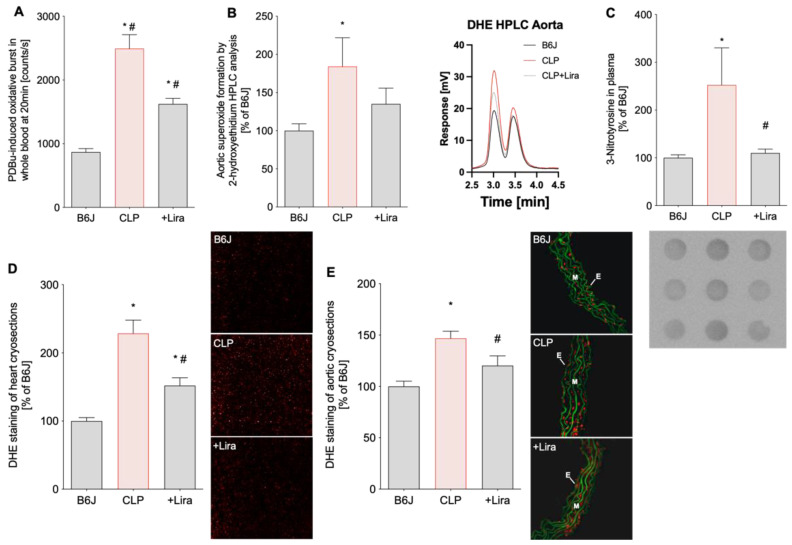
Figure 4.
Treatment with the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide reduces CLP-induced vascular, cardiac and systemic oxidative stress in polymicrobial septic mice. (A) The whole blood oxidative burst was determined by chemiluminescence (L-012) after phorbol ester (PDBu) stimulation. (B) The superoxide-specific DHE product, 2-hydroxyethidium, was quantified in aortic tissue and expressed as a percentage of B6J controls. Representative chromatograms are shown besides the quantification. (C) 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT)-positive proteins in plasma as a consequence of peroxynitrite formation were measured by dot blot analysis. A representative image is shown below the densitometric quantification. (D,E) Cardiac and aortic cryosections were stained with dihydroethidium to visualize ROS formation as red fluorescence and autofluorescence from aortic laminae as green. The representative photomicrographs are shown next to the densitometric analysis. E, endothelium; M, media. Data are the mean ± SEM of 6 individual blood samples (each pooled from 3 to 4 mice) (A), 6-8 (B) and 4 (D,E) measurements from individual animals or 4 individual plasma samples (each pooled from 3 to 4 mice) (C). * p < 0.05 vs. B6J; # p < 0.05 vs. CLP.