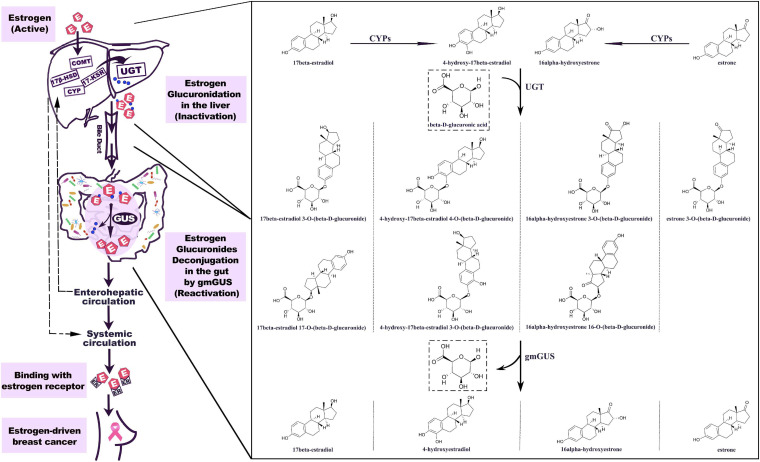
FIGURE 1.
Estrogen metabolism is mediated by GUS. The hepatic metabolism of estrogen is catalyzed by a series of enzymes. Parent estrogens and the phase I metabolites can be conjugated with glucuronic acid by the catalyzation of UGT. The estrogen glucuronides are biologically inactive, but by bile excretion, they enter the gastrointestinal tract where gmGUS liberates estrogens from conjugates. The reactivated estrogens are reabsorbed into the body through the enterohepatic circulation. 7β-HSD, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase; CYP, cytochrome P-450 enzyme; 17-KSR, 17-ketosteroid reductase; UGT, uridine 5′-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase; gmGUS, gut microbial β-glucuronidase; IR, insulin receptor.