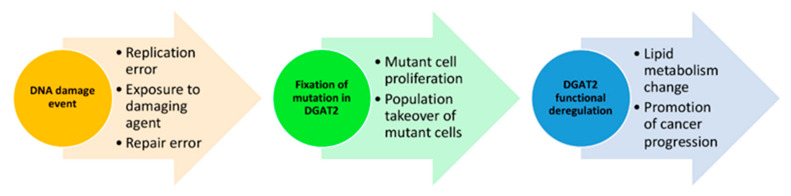
Figure 6.
Model of the functional consequence in cancers linked to DGAT2 mutations. An initial DNA damage event on the sequence of DGAT2 occurs through various mechanisms. DGAT2 pathogenic mutations become fixed in cells that adapt and thrive in specific tissue environments. As the population of DGAT2 mutant cells outcompetes its wild-type counterparts, lipid metabolism changes due to altered function in the DGAT2 protein and associated lipid regulators. Cancer-promoting conditions select for DGAT2 deregulation to contribute to cellular transformation.