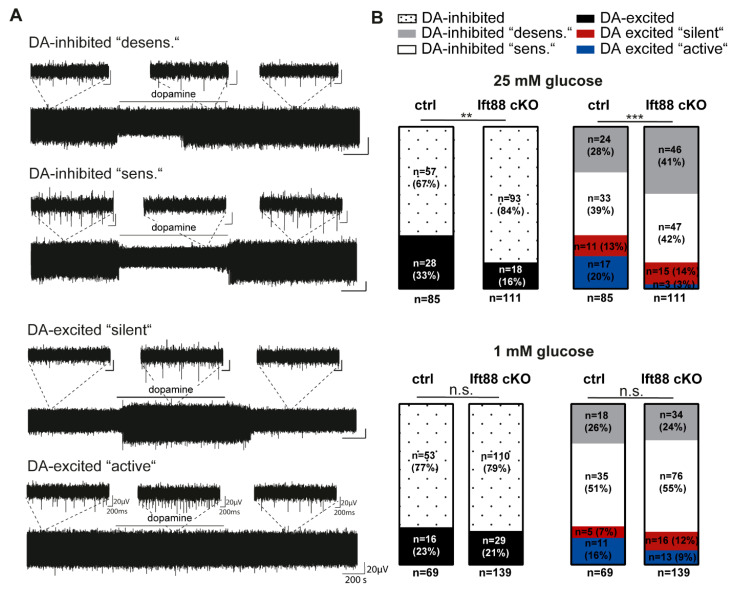
Figure 3.
More SN neurons with inhibitory dopamine responses in Ift88 cKO mice. Spontaneous activities and responses to dopamine (in the figure abbreviated as DA, 100 µM, bath applied for 15 min) of SN neurons in brain slices from adult controls and Ift88 cKO mice, recorded with multi-electrode array techniques (MEA) in ACSF, containing either 25 mM or 1 mM glucose, as indicated. (A) Exemplary traces of the four different types of dopamine responses of SN neurons, as described [5]. Inserts display enlarged traces of two seconds. (B) SN neurons were classified according to their dopamine responses in dopamine-inhibited cells (inhibited pacemaker activity in dopamine), and dopamine-excited cells (increased pacemaker frequency in dopamine) Dopamine-inhibited cells were subdivided in neurons with (“desens.”, grey) and without (“sens.”, white) prominent desensitization of dopamine responses over time. Dopamine-excited cells were subclassified in neurons without (“silent”, red) and with (“active”, blue) spontaneous activity before dopamine application. In saturated glucose (25 mM), Ift88 cKO mice displayed significantly more SN neurons with inhibitory dopamine responses (**, p = 0.0062), compared to controls (ctrl.), due to significantly lower numbers of dopamine-excited neurons of the “active” type (***, p = 0.0001). Statistical comparisons: chi-square tests. Number of analyzed neurons indicated by (n). All values and full statistics are detailed in the supplementary statistical information and Supplementary Table S4.