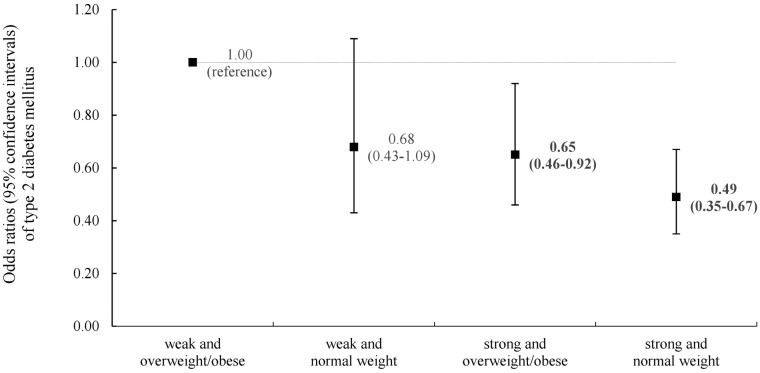
Fig 2. Joint associations of relative grip strength and body mass index with T2DM.
Participants were divided into four groups based on combined categories of relative grip strength (weak or strong) and body mass index (normal weight, overweight/obese), respectively. "Weak" was the lower 20% of relative grip strength and "strong" was the upper 80% of relative grip strength. Normal weight was BMI < 25.0kg/m2, overweight/obese was BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2. The model was adjusted for sex, age (years), smoking status (never, former, current), current alcohol drinking (yes or no), regular exercise (yes or no), living with family (yes or no), ≥high school graduate (yes or no), family history of diabetes (yes or no), hypertension (yes or no), dyslipidemia (yes or no), The number of participants (cases of T2DM) in the “overweight/obese and weak,” “overweight/obese and strong,” “normal weight and weak,”, and “normal weight and strong” groups were 352 (73), 824 (120), 211 (34), and 1,424 (144), respectively.