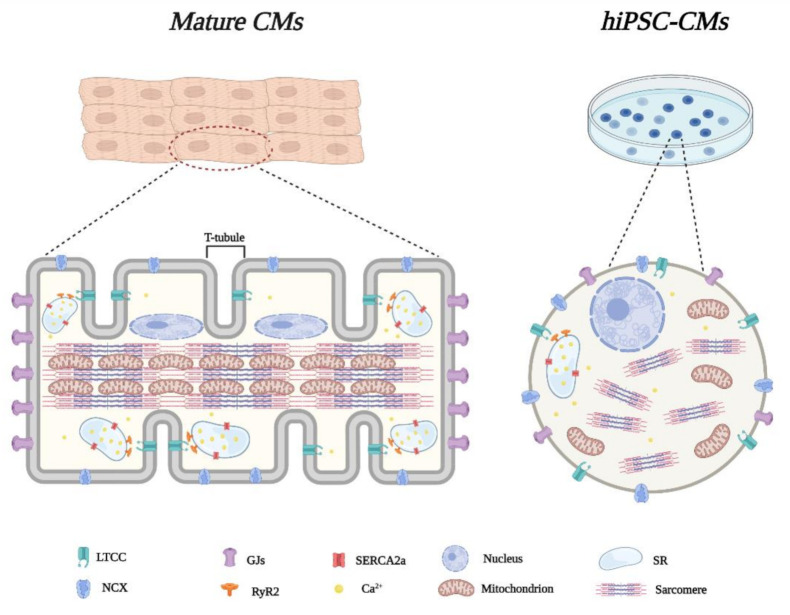
Figure 1.
Principal morphological characteristics of the two cell categories: on the left a mature cardiomyocyte (CM) with a typical rod-shaped structure and specific organization, an elaborate tubular network, a neighboring sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), and large numbers of mitochondria. On the right, the human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC)-CM, which is smaller and more round-shaped, with an immature structure. Compared to adult CM, the hiPSC-CM presents (i) a lower co-localization of the L-type Ca2+ channel (LTCC) with the Ryanodine receptor type 2 (RyR2), (ii) a reduced number of gap junctions (GJs), (iii) an irregular distribution of Ca2+ ions and (iv) the T-tubular structure deficiency and immature sarcomere organization.