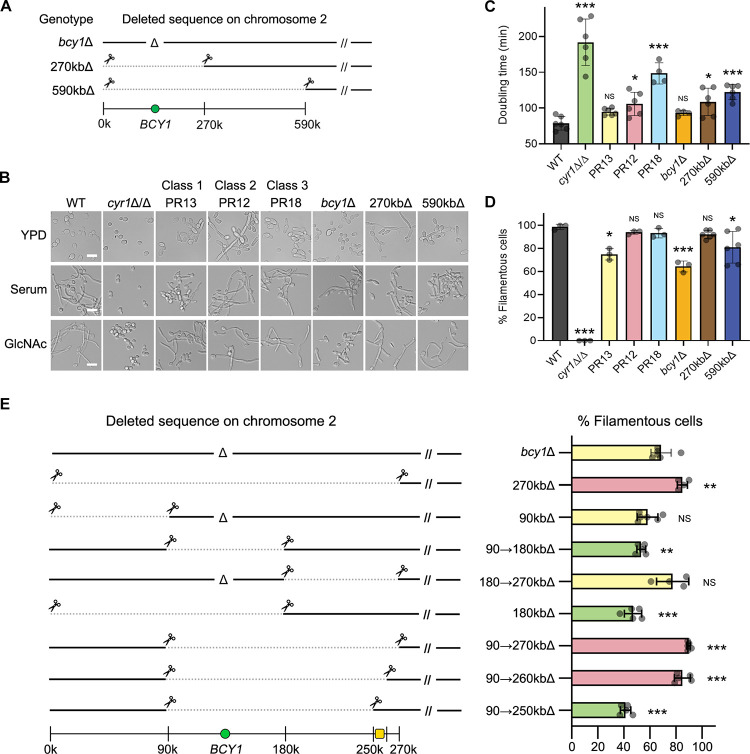
Fig 2. Gene mapping by CRISPR-Cas9 demonstrates that haploinsufficiency of genes in chromosome 2 improved hyphal induction in cyr1Δ/Δ PR mutants.
(A) A schematic diagram showing deleted sequences on chromosome 2. (B) The strains indicated at the top were grown in the liquid medium indicated on the left, and then hyphal induction was assessed microscopically. Cells were grown in liquid medium containing 15% serum or 50 mM GlcNAc to induce hyphal growth at 37°C for 3 h and then photographed. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Doubling times were measured in liquid YPD medium at 30°C. Shown is the mean ± SD of 6 independent experiments. The doubling time of the strains shown was significantly shorter when compared to the cyr1Δ/Δ background (p < 0.01). (D) Graph indicating the percent of filamentous cells after growth in GlcNAc medium described in panel B. Shown is the mean ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments with at least 100 cells counted for each condition. (E) Gene mapping by CRISPR-Cas9 identified a 10-kb region (yellow square) that is involved in the filamentous phenotype. The left panel shows deleted sequences on chromosome 2. The right panel shows the percent of filamentous cells in liquid GlcNAc medium at 37°C; green, weak hyphal induction; yellow, intermediate hyphal induction; pink, strong hyphal induction. (A and E), Note that deletions are heterozygous; the cells retain a wild-type version of chromosome 2. Numbers and symbols indicate gene deletion (Δ), CRISPR cut site (scissors), large genomic deletion (dotted line), BCY1 gene (green circles), and chromosomal position (kb). (C and D) Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test comparing the strains with the WT or parental strain; NS p > 0.05, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.