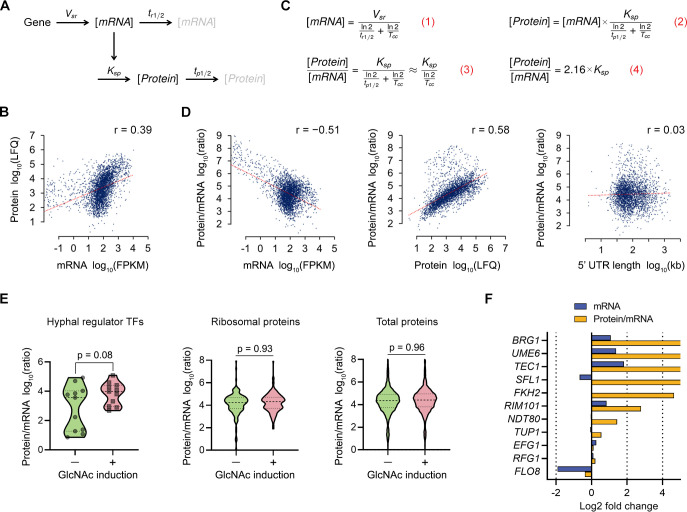
Fig 5. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analyses indicate that hyphal stimulation induces translation of hyphal regulator TFs.
(A) A basic gene expression model with key parameters (adapted from REF. [56,92]). The mRNA is transcribed with rate Vsr and degraded with a half-life represented by tr1/2. The protein is translated proportionally to the mRNA abundance with the rate constant Ksp and degraded with a half-life of tp1/2. (B) An across-gene correlation analysis comparing estimates of absolute mRNA abundance (expressed in fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM)) to protein abundance (expressed as label free quantitation (LFQ)) in exponentially growing WT cells. r, Pearson correlation coefficient. (C) Mathematical expression of mRNA (Eq 1) and protein abundances (Eq 2) as a function of key gene expression parameters, including cell doubling time Tcc, as detailed in REF. [92]. Rearranging Eq 2 yields the dependency of protein-mRNA abundance ratio on the translation rate constant Ksp, cell doubling time Tcc, and protein half-life tp1/2 (Eq 3). We neglected protein degradation assuming that protein replacement is generally driven by dilution due to cell division in exponentially growing C. albicans cells (tp1/2 >> Tcc). Substituting the cell doubling time (Tcc = 1.5 h in C. albicans) yields Eq 4. Therefore, we can approximate the translation rate with the protein-to-mRNA level ratio. (D) Across-gene correlation analyses comparing protein-to-mRNA ratio versus mRNA abundance, protein abundance, and 5’ UTR length (from left to right). r, Pearson correlation coefficient. (E) Protein-to-mRNA ratios of 11 selected hyphal regulator transcription factors (TFs) during GlcNAc induction in WT. The protein-to-mRNA ratios of the 5 hyphal regulators were two orders of magnitude lower than the median in −GlcNAc control, indicating their translation rate was very low before hyphal induction. The p-value was calculated using two-sided unpaired t-test (hyphal regulator TFs) and z-test (ribosomal proteins and total proteins). (F) The relative change in protein-to-mRNA ratio for the selected 11 hyphal regulators is shown in yellow, relative changes in mRNA expression are shown in blue. The protein-to-mRNA ratio of UME6, SFL1, BRG1, TEC1, and FKH2 increased dramatically (log2 fold change > 4) during hyphal induction while mRNA levels did not.