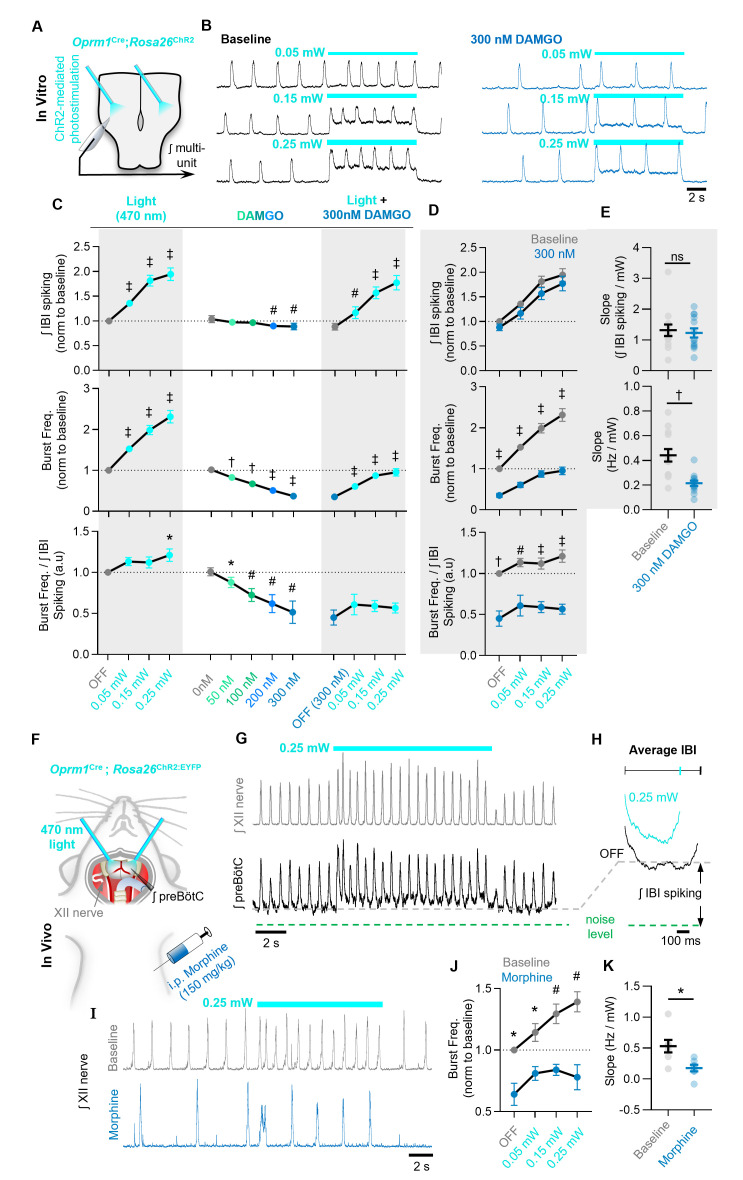
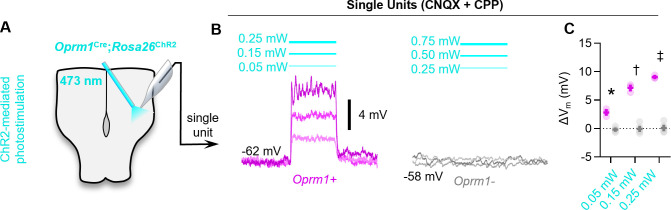
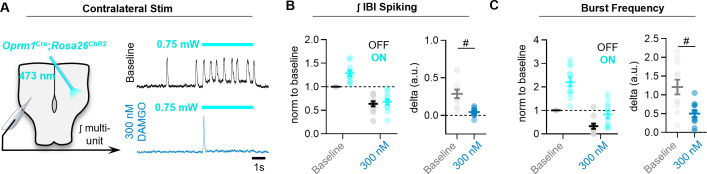
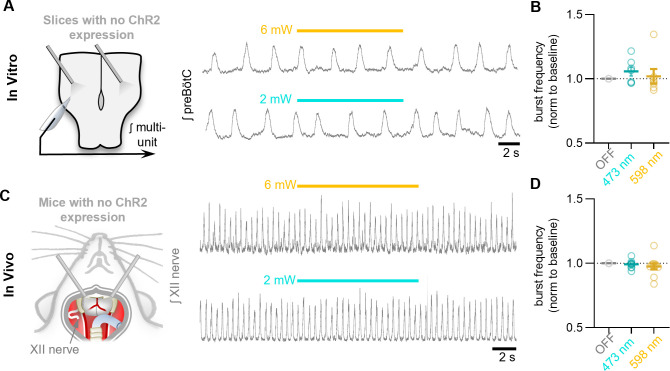
Figure 6. The ability of Oprm1+ neurons to drive preBötC activity is reduced by MOR activation.
(A) Experimental schematic and (B) example preBötC activity at baseline and in 300 nM DAMGO during bilateral photostimulation of Oprm1+ neurons. (C) Quantification of ʃIBI spiking, burst frequency, and the burst frequency/ʃIBI spiking ratio in n=13 slices during baseline photostimulation of Oprm1+ preBötC neurons (RM one-way ANOVA of ʃIBI spiking [p<0.0001], RM one-way ANOVA of frequency [p<0.0001], RM one-way ANOVA of frequency/ʃIBI spiking ratio [p=0.038]) during increasing concentrations of DAMGO (RM one-way ANOVA of ʃIBI spiking [p=0.0009], RM one-way ANOVA of frequency [p<0.0001], RM one-way ANOVA of frequency/ʃIBI spiking ratio [p=0.003]), and during photostimulation in 300 nM DAMGO (RM one-way ANOVA of ʃIBI spiking [p<0.0001], RM one-way ANOVA of frequency [p<0.0001], RM one-way ANOVA of frequency/ʃIBI spiking ratio [p=0.112]). (D) Comparison of light-induced changes in IBI spiking, burst frequency, and the burst frequency/IBI spiking ratio. Data corresponds to gray highlighted regions in (C) (RM two-way ANOVA of ʃIBI spiking [p=0.165], RM two-way ANOVA of frequency [p<0.0001], RM two-way ANOVA of frequency/ʃIBI spiking ratio [p<0.0001]). (E) Quantified slope of IBI spiking and burst frequency responses to increasing power of light stimulations (paired two-tailed t-tests). (F) Schematic of in-vivo preparation and (G) representative ʃXII and ʃpreBötC activity during 10 s bilateral photostimulation of Oprm1+ neurons. (H) Averaged ʃIBI activity at baseline (OFF) and during photostimulation. (I) Example inspiratory rhythm (XII) during bilateral photostimulation at baseline and following i.p. morphine. (J) Quantified changes in inspiratory frequency evoked by photostimulation at baseline and after morphine from n=five anesthetized mice (RM two-way ANOVA [p=0.0003]). (K) Quantified slope of burst frequency responses to increasing power of light stimulations (paired two-tailed t-test). Significance of post hoc tests: ns=not significant, *p<0.05, #p<0.01, †p<0.001, ‡p<0.0001.