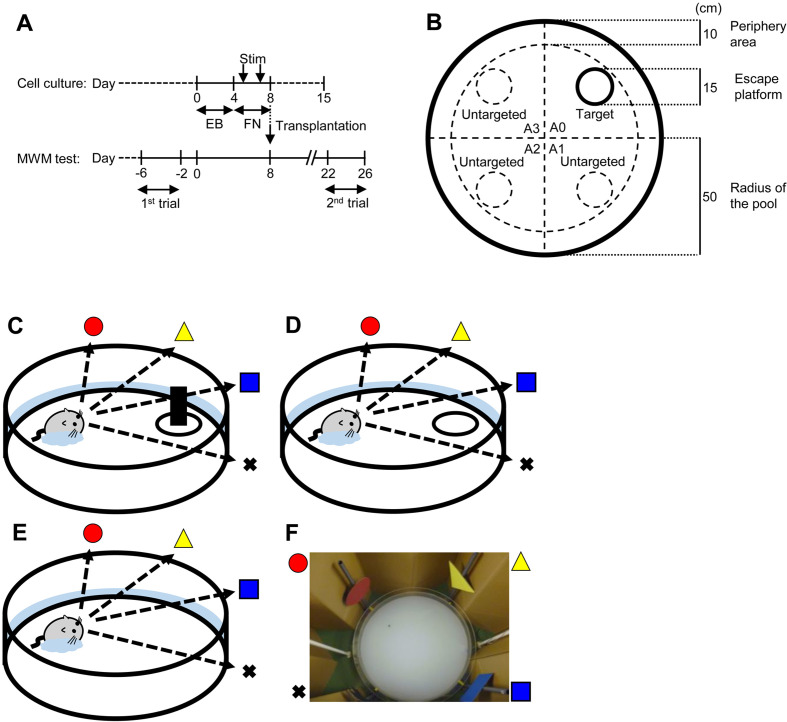
Fig. 1.
Schematic representations of human iPS cell-derived neural cell induction and functional assessment by Morris water maze test. (A) Neural induction and transplantation of of hiPS cells. Undifferentiated hiPS cells maintained with mouse embryonic fibroblasts were developed into EBs by 4-day floating culture. To differentiate neural cells, EBs were stimulated with RA, NOG, and SHH at days 5 and 7 (Stim) on a fibronectin (FN)-coated plate. The cells contained neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs), as previously reported. For measuring neurotransmitter secretion, culture supernatants of NSPCs were collected at days 5, 8, and 15 for applying ELISA. At day 8, NSPCs were transplanted into PDAPP Tg mice (n=28). Cognitive functions of the grafted PDAPP Tg mice were assessed by MWM test before (1st trial: from day −6 to day −2) and after (2nd trial: from day 22 to day 26) transplantation. (B) The MWM was conducted using a circular pool (diameter: 100 cm) with opaque water and a plastic escape platform (diameter: 15 cm). A 10-cm-wide banded zone along the wall was defined as the peripheral area for behavioral analysis. (C–E) Mice were subjected to the MWM test for 6 consecutive days as follows: (C) visible test on the first day using a platform visualized with a black bottle; (D) hidden test on 4 consecutive days using a platform without the black bottle submerged below the surface of the opaque water; and (E) probe test on the last day under the same conditions except that the platform was removed. The swimming trajectory was monitored by a CCD camera and recorded with a PC. (F) Picture of the experimental equipment for the MWM test.