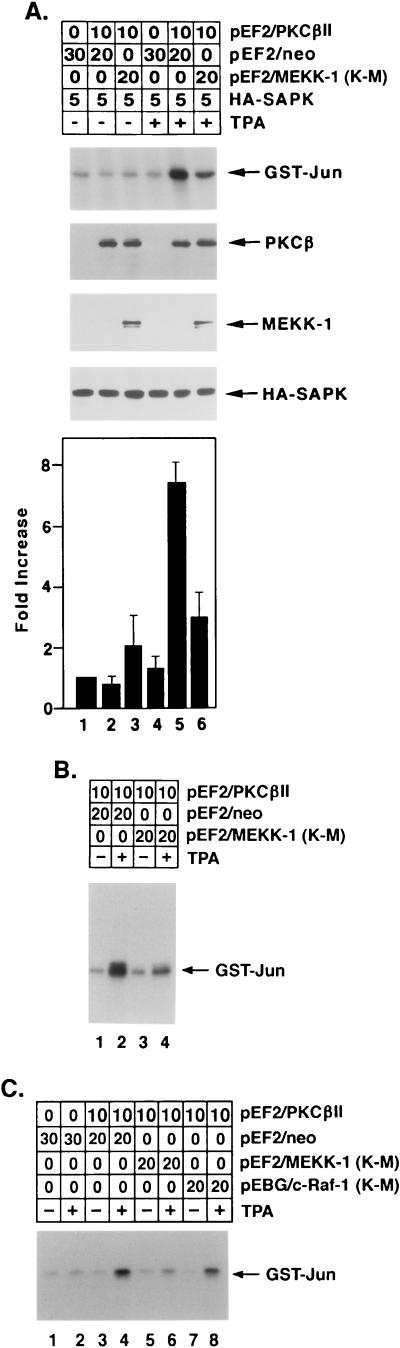
FIG. 10.
TPA-induced activation of SAPK by a PKCβII- and MEKK-1-dependent mechanism. (A) HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated amounts of pEF2/PKCβII, pEF2/neo, pEF2/Flag-MEKK-1 (K-M), and HA-tagged SAPK. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were left untreated or were treated with 16 nM TPA for 15 min. Anti-HA antibody immunoprecipitates were assayed for phosphorylation of GST-Jun. Lysates of the transfected cells were also subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-PKCβII, anti-Flag M2, and anti-HA antibodies to assess the levels of expression of transfected PKCβII, Flag-MEKK-1 (K-M), and HA-tagged SAPK. The levels of GST-Jun phosphorylation were quantitated on the basis of the intensity of the signals, and the results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of three independent experiments (lowest panel). (B) HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated amounts of pEF2/PKCβII, pEF2/neo, and pEF2/Flag-MEKK-1 (K-M). HA-tagged SAPK was not transfected in this experiment. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were left untreated or were treated with 16 nM TPA for 15 min. Anti-SAPK antibody immunoprecipitates were assayed for phosphorylation of GST-Jun. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated amounts of pEF2/PKCβII, pEF2/neo, pEF2/Flag-MEKK-1 (K-M), and pEBG/c-Raf-1 (K-M). At 48 h posttransfection, cells were left untreated or were treated with 16 nM TPA for 15 min. Anti-SAPK antibody immunoprecipitates were analyzed for phosphorylation of GST-Jun.