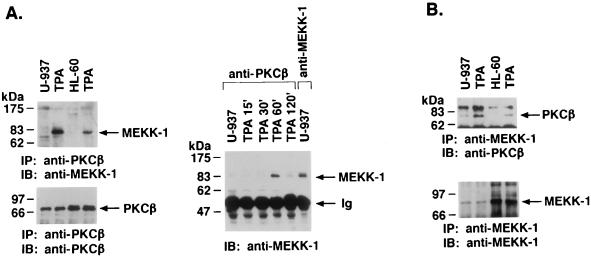
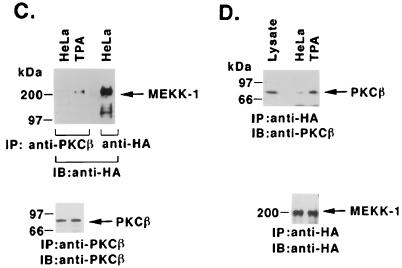
FIG. 7.
TPA-induced association of PKCβII and MEKK-1. (A) U-937 and HL-60 cells were treated with 16 nM TPA for 1 h (left panel) or for the indicated times (right panel). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKCβII or anti-MEKK-1 antibody (11612; right panel, last lane). The immunoprecipitates (total applied to each lane) were subjected to immunoblot (IB) analysis with anti-PKCβII or anti-MEKK-1 antibody. Half of the anti-MEKK-1 antibody immunoprecipitate was applied to the right panel, last lane. Ig, immunoglobulin. (B) U-937 and HL-60 cells were treated with 16 nM TPA for 1 h. Anti-MEKK-1 antibody immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-PKCβII or anti-MEKK-1 antibody. (C and D) HeLa cells were cotransfected with 10 μg of pEF2/PKCβII and 10 μg of HA-tagged full-length MEKK-1. At 48 h after transfection, the cells were treated with 16 nM TPA for 15 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKCβII (C) or anti-HA (D) antibody and then subjected to immunoblot (IB) analysis with anti-HA (C) or anti-PKCβII (D) antibody. As a control, lysates were subjected directly to immunoblotting with anti-PKCβII antibody (left lane in panel D).