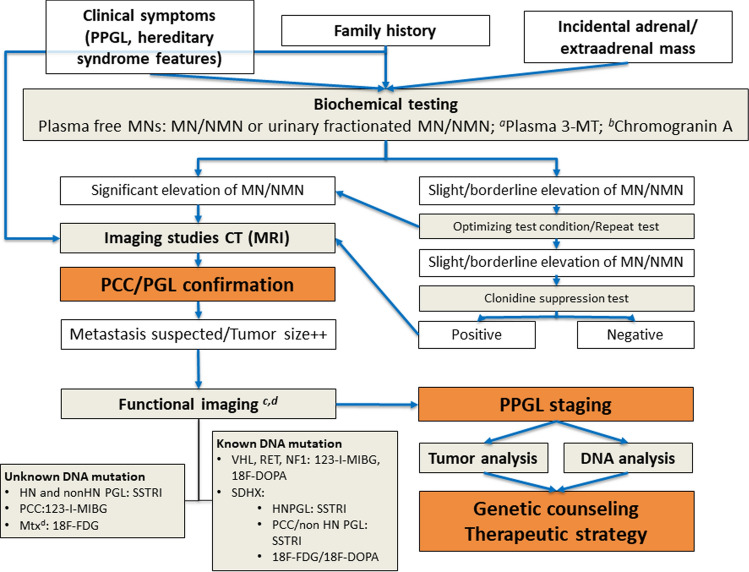
Fig. 1.
Diagnostic algorithm for PPGLs. CT computed tomography, FDG fluorodeoxyglucose, HNPGL head and neck paraganglioma, MN metanephrine, Mtx metastasis, NMN normetanephrine, MIBG metaiodobenzylguanidine, 3-MT 3-methoxytyramine, MRI magnetic resonance imaging, PCC pheochromocytomas, PGL paragangliomas, PPGL pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas, SSTRI somatostatin receptor imaging, VHL von Hippel-Lindau. a Plasma 3-MT: only in high clinical suspicion of dopamine-secreting tumors/hereditary syndromes associated with HNPGL. b Chromogranin A: nonspecific neuroendocrine tumor marker that may be considered if high clinical suspicion of silent PPGLs. c Recommended at diagnosis only in cases of high suspicion of metastasis, particular if there is family history or silent tumor. d 123-I-MIBG versus 111In/99mTc/68 Ga SSTRI, is recommended before MIBG versus radionuclide-SSTR analogs treatment