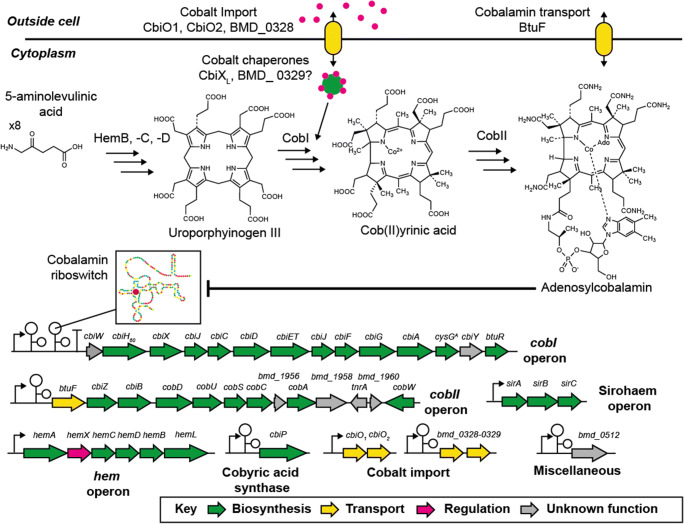
Fig. 2.
Summary of cobalamin genetics, biosynthesis, and regulation in Priestia megaterium DSM319. Upper part: cobalt and cobalamin transporters are indicated in yellow, cobalt in pink, and cobalt chaperon in green. Middle part: summary of cobalamin biosynthesis starting from 8 molecules of 5-aminolevulinic acid. The final product here is shown as adenosylcobalamin which can interact with the cobalamin riboswitches. CobI and CobII indicate all enzymes encoded by the cobI and cobII operons shown below. Lower part: all genes are represented as colored arrows. Black arrows upstream of the operons/single genes indicate promoters, black “T”s terminators and black stem-loop structures cobalamin riboswitches. All genes clustered in operons or situated on their own are annotated. Hypothetical genes are annotated as open reading frames (bmd_0000) as shown in www.megabac.tu-bs.de.