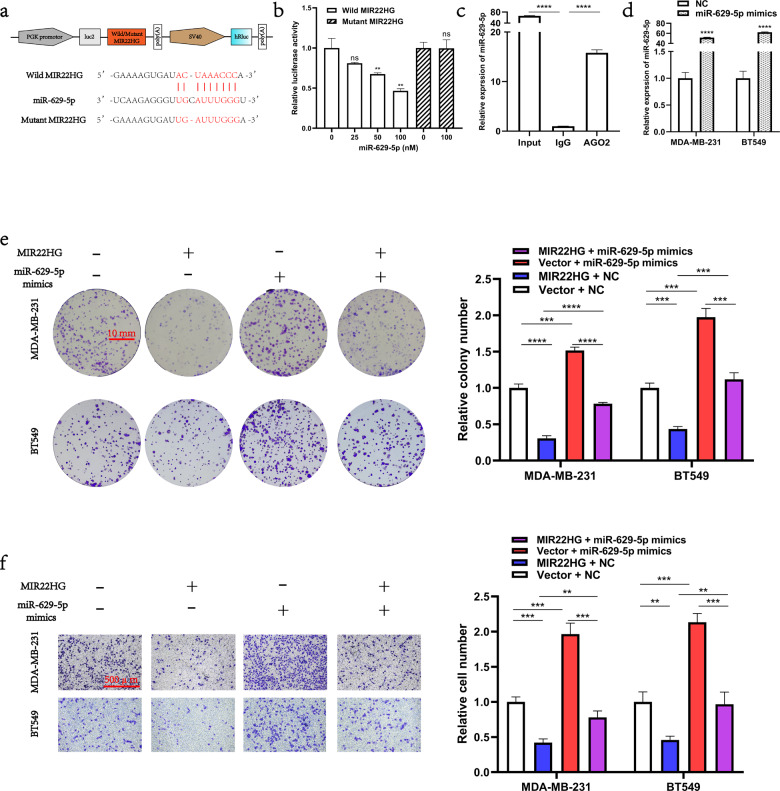
Fig. 4. MIR22HG functions as an miR-629-5p sponge in breast cancer cells.
a Schematic diagram of the interaction between miR-629-5p and wild-type/mutant MIR22HG. b Dual-luciferase assays in HEK293T cells co-transfected with wild-type/mutant MIR22HG and miR-629-5p mimics (25, 50, and 100 nM) or NC. At 48 h after transfection, the 293 T cells were collected for the detection of firefly luciferase activity, with Renilla luciferase activity as internal control. c AGO2 immunoprecipitation assay was performed using HEK293T cells to detect the expression of miR-629-5p associated with AGO2. The AGO2-specific antibody was applied to precipitate the AGO2-RNA complex after MIR22HG overexpression in 293T cells. Total RNA was extracted, and real-time PCR was performed to determine the expression of miR-629-5p associated with AGO2, using IgG-specific antibody as negative control. d Overexpression efficiency of miR-629-5p was analyzed by real-time PCR after MDA-MB-231 and BT549 cells were transfected with miR-629-5p mimics or NC. e The effects of MIR22HG and miR-629-5p co-transfection on the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 and BT549 cells were evaluated by colony formation assay (18-day period). f The effects of MIR22HG and miR-629-5p co-transfection on the migration of MDA-MB-231 and BT549 cells were evaluated by Transwell assay (20-h period, 3 × 104 cells per well, 100× magnification). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. All experiments were repeated thrice.