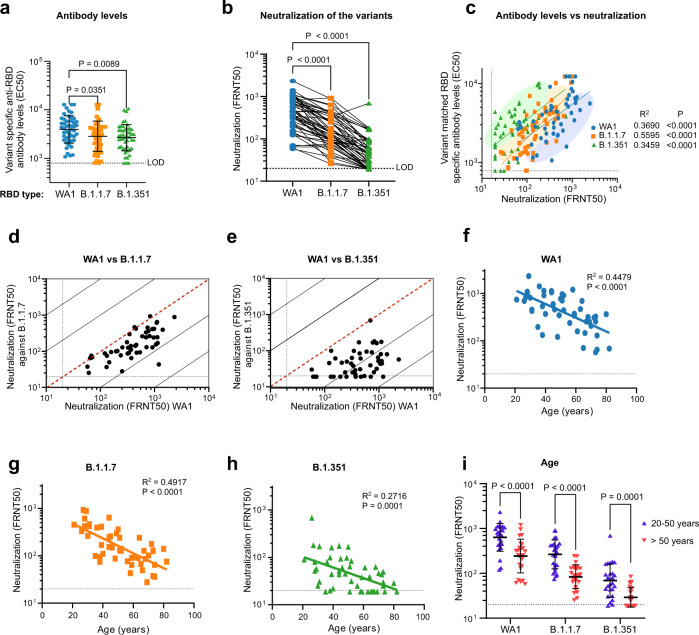
Fig. 1. Serum antibody levels of BNT162b2 vaccine recipients and potency of sera to neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants.
a Serum antibody levels (EC50) that recognize the spike RBD of the wild-type USA-WA1/2020 (WA1) (Blue circles), B.1.1.7 (Orange squares), and B.1.351 (Green triangles) variants are shown. The RBD-B.1.1.7 carries the N501Y mutation, the only RBD mutation present in the B.1.1.7 variant. The RBD-B.1.351 has the K417N, E484K, and N501Y mutations which are the only three RBD mutations present in the B.1.351 variant. n = 51 biologically independent samples. b Comparison of neutralization titers (FRNT50) between WA1, B.1.1.7 (P = 0.0351) and B.1.351 (P = 0.0089) for BNT162b2 vaccinee sera. n = 50 biologically independent samples. c Correlation of variant matched RBD-specific antibody levels and neutralization titers (FRNT50) of the WA1 virus and the two variants. d, e Correlations between neutralization titers of the B.1.1.7 (d) and B.1.351 (e) variants with the WA1 virus. The dotted diagonal lines indicate identical neutralization, and the solid diagonal black lines indicate 10-fold differences in neutralization. f–h Correlation between participant age and neutralization titer against WA1 (f) (P < 0.0001), B.1.1.7 (g) (P < 0.0001), and B.1.351 (h) (P < 0.0001). n = 50 biologically independent samples. i Effect of age range 20–50 years (blue triangle) and >50 years (red inverted triangle) on the neutralization potency among the BNT162b2 vaccine recipients (WA1,B.1.1.7 P < 0.0001, B.1.351 P = 0.0001). n = 25 biologically independent samples per age group. For a, b, f–i, data are presented as the mean ± SD of log transformed values; P values are two-sided and include a Šidák multiple comparison correction. All experiments were performed in duplicate.