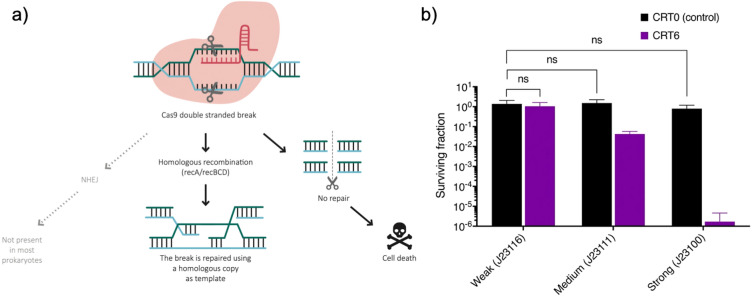
Figure 2.
Mechanism of CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials and killing efficiency of different expression levels of SpCas9. (a) SpCas9-double stranded break results in DNA damage. In order to repair it, most prokaryotes rely almost exclusively on RecA-mediated HR using an intact copy as substitute DNA template, however if the DNA damage is not repaired the consequences are lethal for the cell. In the context of CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials, cell death is the outcome when the DNA damage is faster than the repair mechanisms of the cell. (b) The fraction of bacteria surviving SpCas9-mediated death was determined by plating the same dilution of cells on agar plates with and without the inducers (2 mM of theophylline and 1% arabinose). CRT0 (control) is a guide RNA that has no target site in the chromosome of E. coli MG1655. CRT6 is a gRNA with a single target site. SpCas9 was expressed from 3 promoters with distinct expression strength based on the scores from the Anderson collection (http://parts.igem.org/Promoters/Catalog/Anderson): weak (J23116), medium (J23111) and strong (J23100) promoters.