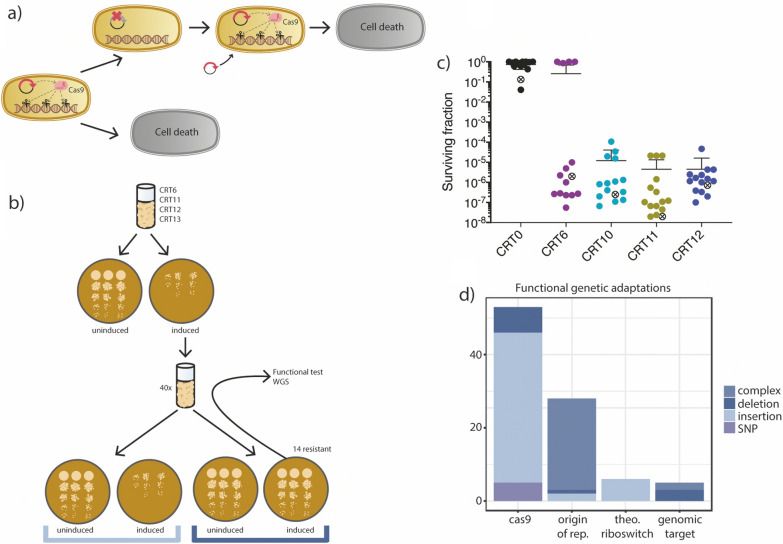
Figure 3.
Reintroduction of CRISPR-Cas antimicrobial. (a) Schematic description of plasmid re-introduction. After SpCas9 induced death, escaper cells have inactivated the antimicrobial by mutating cas9. In order to re-sensitize the cells, a new SpCas9 plasmid is delivered to the escape mutants. (b) Workflow for re-introduction of CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials and selection of mutants for whole genome sequencing analysis (WGS). (c) Surviving fraction of 14 mutants after reintroduction of an intact spCas9 copy. (d) Frequency of complex mutations, deletions, insertions and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on the cas9 carrying plasmid pCasens3 and at the genomic target sites of CRT0 (fucI) and CRT6 (fadD) identified for each sequenced lineage. Complex mutations include a combination of multiple structural variants or inversions, as defined by CLC Genomic Workbench. 14 biological replicates were included of CRT0, CRT6, CRT11, CRT12 and CRT13 as well as a uninduced control.