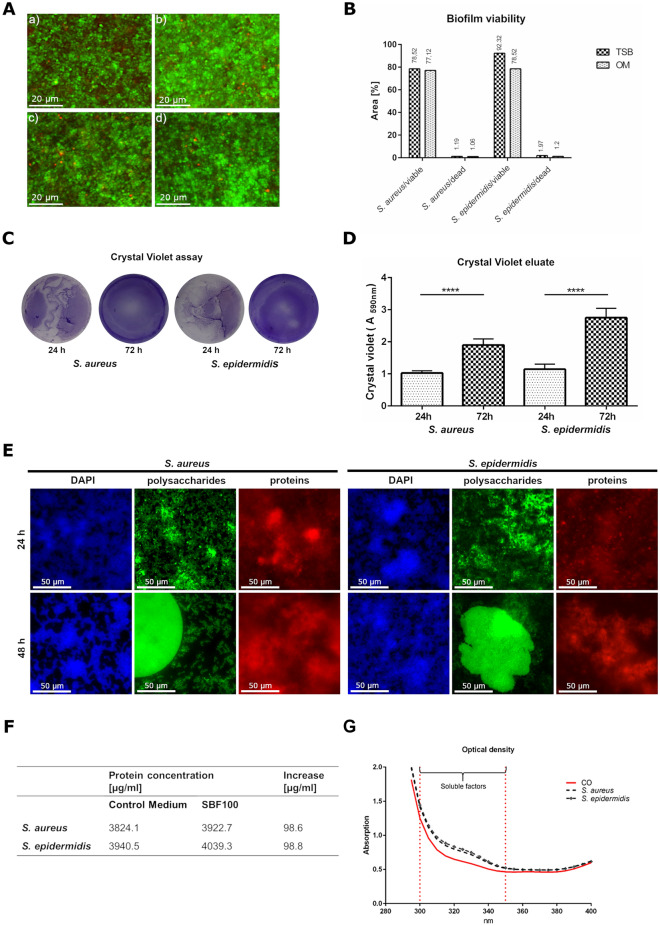
Figure 1.
Biofilm characterization and the concentration of SBF in OM. S. aureus (A, a) and S. epidermidis (A, b) after 48 h incubation in 3% TSB. S. aureus (A, c) and S. epidermidis (A, d) after 48 h incubation in OM. Bacteria with intact cell membranes stained fluorescent green (SYTO 9, ex/em 480/500 nm). Bacteria with damaged membranes stained fluorescent red (propidium iodide ex/em 490/635 nm). The viability of S. aureus and S. epidermidis in 3% TSB and OM was calculated using ImageJ and revealed comparable results (B). The crystal violet assay detects the biomass growing over 72 h (C) and the measured crystal violet eluate confirmed these results (D). Major components of the biofilm, polysaccharides were stained with Concanavalin A, conjugated with Alexa 488 (ex/em 470/525 nm), proteins were detected by SYPRO Ruby Biofilm Matrix stain (ex/em 450/610 nm) and the DNA was visualized by DAPI (ex/em 358/461 nm) (E). The BCA assay revealed a similar increase of nearly 100 µg protein /ml in the OM with SBF from S. aureus and S. epidermidis (F). The measurement of optical density confirmed the results of the protein concentration (G).