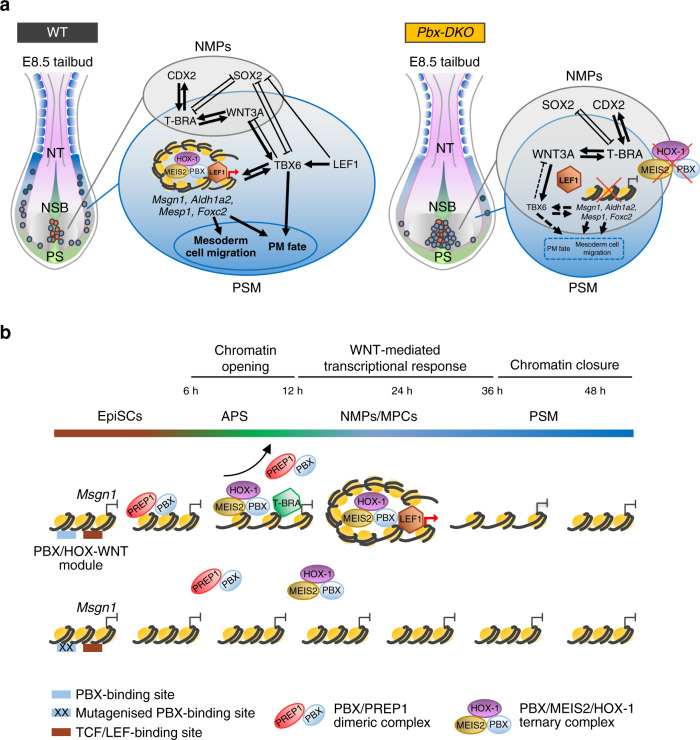
Fig. 8. TALE complexes promote WNT-mediated transcriptional response in paraxial mesoderm.
a Schematics of the molecular networks at play in the E8.5 embryonic tailbud. Left: cartoon showing NMPs (red dots) transitioning to MPCs (light blue dots) and migrating to the PSM (blue) in WT embryos. GRNs governing the balance between NMP expansion in the CLE (grey) and PSM differentiation (blue) are illustrated. The TALE complexes and LEF1 bind cooperatively to the regulatory regions of PM genes, like Msgn1, Aldh1a2, Mesp1 and Foxc2, promoting their expression. The activation of the PM programme ultimately controls migration of MPCs from the progenitor zone to the PSM and the acquisition of PM fate. Right: PBX loss (yellow) results in reduced mobility of the MPCs and accumulation of NMPs-MPCs in the progenitor zone, leading to enlarged tailbuds and reduced PSM formation. Failure of TALE complex assembly on the regulatory regions of PM genes impairs LEF1 recruitment and activation of the GRN promoting PSM formation. In contrast, the molecular circuits sustaining NMP expansion are maintained by positive feedback loops. Of note, the observed PBX-LEF1 binding to the N1 repressive element of the Sox2 regulatory region suggests that PBX and LEF1 cooperative activity could repress Sox2 expression (Fig. 5e) and NMP maintenance. Thus, PBX proteins are required for the transition of NMPs to PSM, playing essential and previously unappreciated roles in the early stages of somitogenesis. CLE caudal lateral epiblast, NSB node-streak border, PS primitive streak, PSM pre-somitic mesoderm, NT neural tube. b Model of the transcriptional activation of Msgn1. Msgn1 regulatory region becomes accessible at 12 h following the collaborative pioneering activity of T-BRA and the TALE complexes. Low-affinity PBX/PREP1 dimers are recruited first and could serve as HOX-1 attractors, or assist the loading of the high-affinity PBX/MEIS2/HOX-1 ternary complex, whose cooperative binding displaces nucleosomes and generates the suitable chromatin context for LEF1 recruitment. Single-base substitutions at the PBX/HOX-1-binding site abrogate accessibility of both PBX/HOX-1 and LEF1-binding regions, emphasising the role of TALE complexes as modulators of chromatin accessibility on WNT-responsive elements.