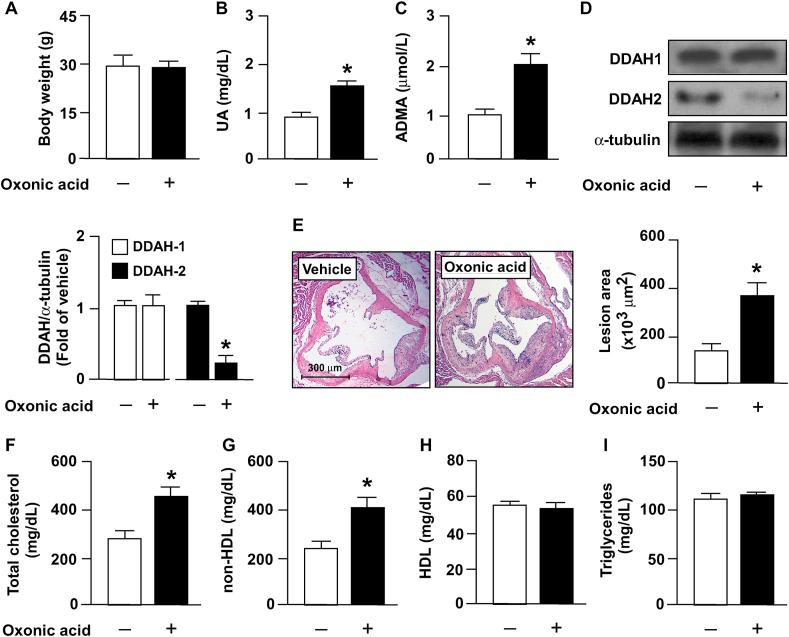
Fig. 5.
Treatment with oxonic acid deregulates ADMA/DDAH-2 pathway and induces atherosclerosis progression in apoe−/− mice. Four-month-old apoe−/− mice received daily treatment with oxonic acid (10 mg/kg body weight) or saline (vehicle control) through gastric gavage for 4 weeks. (A) Protein levels of DDAH-1, DDAH-2, and α-tubulin in aortas. (B) Body weight. (C) Plasma levels of uric acid. (D) Plasma levels of ADMA. (E) Atherosclerotic lesion at the aortic root. (F–I) Serum levels of total cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Data are expressed as means ± SEMs of 10 mice. *Statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) relative to vehicle-treated apoe−/− mice.