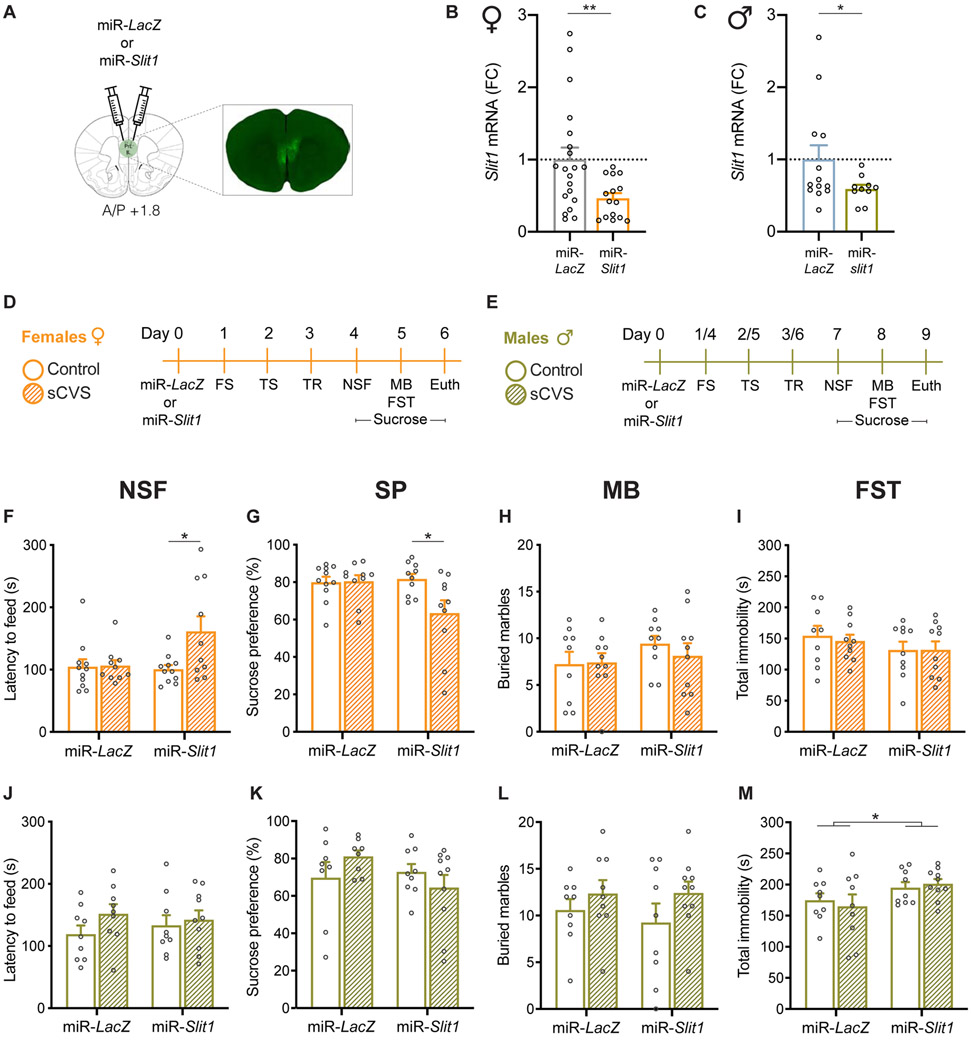
Figure 2. Slit1 KD in vmPFC neurons controls a sex-specific anxiety- and depression-like phenotype in mice.
(A) Schematic representation of viral delivery to KD Slit1 in mouse vmPFC. (B, C) Quantification of HSV-mediated knockdown of Slit1 in the vmPFC validates significant downregulation in female (B) and male (C) mice (n=10-20). (D, E) Schematic representation of the experimental design in female (D) or male mice (E) including surgery, exposure to subthreshold chronic variable stress (sCVS), and behavioral tests used to assess the impact of Slit1 KD compared to controls. (F, J) Slit1 KD in the female vmPFC followed by sCVS increased latency to feed in the novelty suppressed feeding (NSF) test compared to their unstressed counterparts as well as unstressed controls (F), but had no effect in males (J). (G, K) miR-Slit1 sCVS females consumed less sucrose as measured in the sucrose preference (SP) test compared to all the other groups (G), with no effects observed in males (K). (H, L) No differences in the marble burying (MB) test in both females (H) and males (L). (I, M) No differences in the forced swim test (FST) in females (I), but increased immobility time in miR-Slit1 males compared to controls. (M). *p<0.05. Data are shown as means ± s.e.m.