FIG. 4.
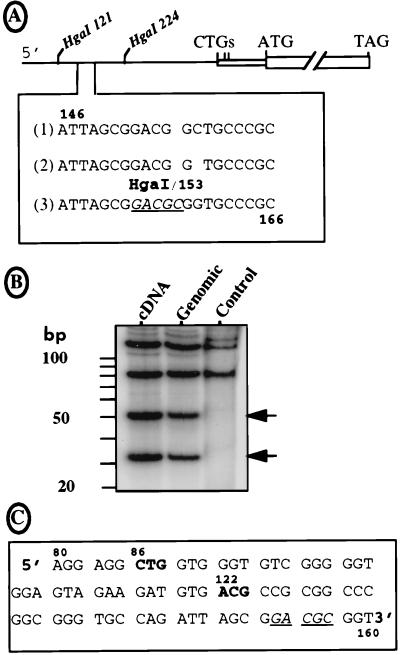
Sequence of the FGF-2 mRNA leader. (A) The sequence of the FGF-2 cDNA 5′ region was obtained by using a DNA analyzer (see Materials and Methods) and compared to the two published sequences. Under the schema of the FGF-2 cDNA indicating the two HgaI sites at positions 121 and 224 downstream from the 5′ end are represented the three sequences of the region from 146 to 166. Lines 1 and 2 correspond to the published sequences of the cDNA and genomic DNA, respectively (41, 44). Line 3 is the sequence obtained in this study for both DNAs with the DNA analyzer. The new HgaI site is underlined (position 153). (B) The pFC1 plasmid with the 5′ region of the FGF-2 cDNA, its homolog with the corresponding genomic sequence (kindly provided by R. Florkiewicz), and a pFC1-derived plasmid lacking the HgaI site at position 153 (point mutations change nt 153-GACGCGG to 153-GATGGC; published for its in-frame ATG-154 [47]) were BssHII digested. The 291-nt-long resulting fragments were dephosphorylated, kinase treated in the presence of [32P]ATP, and then digested with enzyme HgaI. Each step was followed by a G50 column purification. The restriction fragments were fractionated on a 15% polyacrylamide–Tris-borate-EDTA gel, which was dried and autoradiographed. Sizes of the expected fragments are (i) 121, 85, 51, and 34 nt in the presence of the new HgaI site and (ii) 121 nt plus a doublet at 85 nt in its absence. The DNA origin (cDNA or genomic) is indicated at the top; control corresponds to the plasmid lacking the HgaI site at position 153. (C) Representation of the new reading frame given by the DNA sequence shown in A (line 3). The sequence between nt 80 and 163 is shown. The two potential initiation codons are shown in boldface; the HgaI site (positions 153 to 157) is underlined.