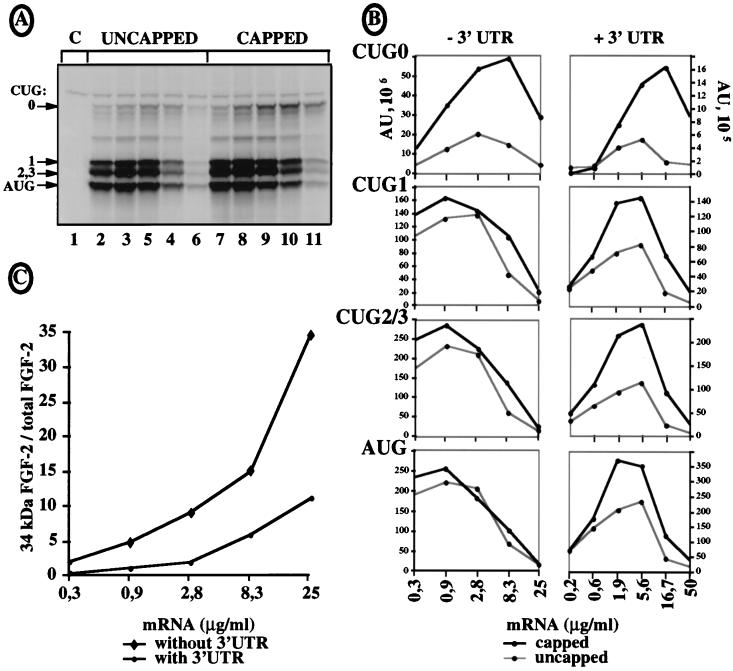
FIG. 6.
Cap dependence of 34-kDa FGF-2 expression. Capped and uncapped FGF-CAT mRNAs, with or without the FGF-2 mRNA 3′ UTR, were transcribed in vitro 2, and different dilutions of each mRNA were translated in RRL in the presence of [35S]methionine and analyzed as for Fig. 5. (A) Autoradiography after PAGE analysis of FGF-CAT mRNA expression. The mRNA was transcribed in vitro from plasmid p5′CAT-A1, in which the first 539 nt of FGF-2 cDNA were fused to the CAT sequence and the shortest FGF-2 3′ UTR (90 nt long). The results correspond to representative experiments that were repeated five times, either with a 90-nt-long 3′ UTR (p5′CAT-A1) or with no 3′ UTR (p5′CAT-A0). Migrations of the size standards and of FGF-CAT proteins are indicated (CUG 0 represents the largest isoform). C (lane 1) is the control without mRNA. FGF-CAT mRNA amounts used in each sample were 0.3, 0.9, 2.8, 8.3, and 25 μg/ml for lanes 2 to 6 (uncapped RNAs) and lanes 7 to 11 (capped RNAs), respectively. (B) FGF-CAT isoform expression using capped and uncapped mRNAs in which the 90-nt-long FGF-2 3′ UTR (−3′ UTR, corresponding to panel A) or the 5,823-nt-long FGF-2 3′ UTR (+3′ UTR) was quantified by PhosphorImager analysis (ImageQuant software). Expression of each isoform from capped or uncapped mRNA is shown in a separate plot. The data are from representative experiments that were repeated at least five times. (C) Ratio of 34-kDa FGF-2 isoform versus total FGF-2 expression in the presence or absence of a 3′ UTR, calculated for capped mRNAs from experiments shown in panel B (expressed as percentage of total FGF-2 expression).